written by Adeel Abbas
Modern Periodic Table-Groups, Periods, Families, and Blocks
Table of Contents
The modern periodic table contains all the elements arranged on the basis of increasing order of their atomic number.
The following table is the modern periodic table.
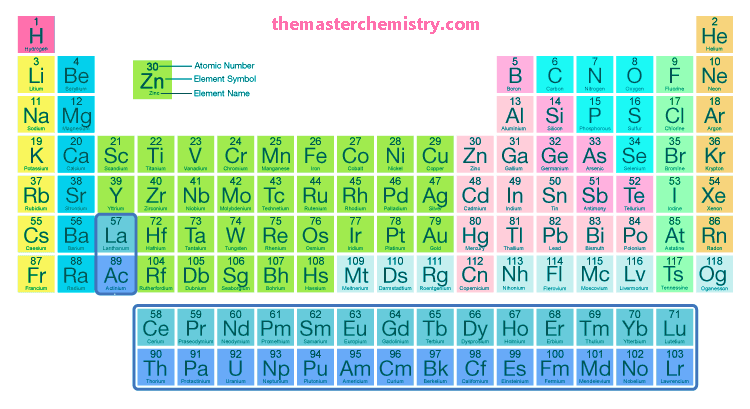
Essential features of the modern periodic table
Groups of the modern periodic table
Elements with similar properties were placed in the vertical column which were called groups
Also read: Development and History of periodic table-A brief overview
Watch the video lecture to better understand about Modern periodic table
Essential features of the groups in the modern periodic table
There are 9 groups in all including group VIIIA of transition elements metals and the zero group of inert gases
Group I to VII are subdivided into sub-group A and B.
- The elements of groups I-A, II-A, etc, Have their outermost shell incomplete while each of their inner shells is complete. they are good metals.
- The elements of group I-A, II-A, IIIA, IVA, VA, VI-A, VII-A, and VIII-A (zero) Consist of some metals some non-metals, and others are metalloids.
- The elements of group IB to VII B and VIIIB Have their two outermost d sub-shell incomplete. they are called transition elements are metals. These are placed in the middle of the modern periodic table. These all are are metals.
- The elements of the zero group have their shells completely filled. they are placed at the extremely right position of the periodic table. These behave as gases at room temperature. These are also called noble gases.
Periods of the modern periodic table
There are 7 periods in the periodic table. let us discuss them one by one.
Period one
First period contain only two elements that is hydrogen and helium. hydrogen is a normal element while helium is an inert pair.
Period 2
The second period contains 8 elements. It is called the short period. The elements are from Lithium to neon As given below.
| Li3 | Be4 | B5 | C6 | N7 | O8 | F9 | Ne10 |
Among these elements for two elements are S block elements next six are from p block elements and the last element neon belongs to P block is an inert gas. The repetition of properties occurs after the 8th element.
Period 3
This period contains also 8 elements. It is called a short period. These elements are from sodium to Argon.
| Na11 | Mg12 | Al13 | Si14 | P15 | S16 | Cl17 | Ar18 |
The first two elements are F block elements next 6 elements are from the P block and the last element Argon is an inert gas. The repetition occurs after eight elements where Lithium resembles Sodium, Be with Mg, B with Al, and F with Cl. They are also A sub-groups.
Period 4
This period contains eighteen elements. This is called a long period. The elements are from K19 to Kr36.
| K19 | Ca20 | Sc21 | Ti22 | V23 | Cr24 | Mn25 | Fe26 | Co27 |
| Ni28 | Cu29 | Zn30 | Ga31 | Ge32 | As33 | Se34 | Br35 | Kr36 |
The first two elements are from S-block. Next 10 elements are from d-block and next six elements are from p-block. The last element Kr belongs to Nobel gases.
This is the first period of the periodic table that involves d-block elements, 3d sub-shell in the process of completion for d-block elements. The repetition of properties occurs after 18 elements. 10 elements are transition elements and 8 are representatives.
Period 5
This period contains eighteen elements. This is called along period. The elements are from Rb37 to Xe54.
| Rb37 | Sr38 | Y39 | Zr40 | Nb41 | Mo42 | TC43 | Ru44 | Rh45 |
| Pd46 | Ag47 | Cd48 | In49 | Sn50 | Sb51 | Te52 | I53 | Xe54 |
The first two elements are from S-block. Next ten elements are from d-block, and next six elements are from p-block. The remaining one Xe is a nobel gas.
In this period, d-block elements are also there and are called transition elements. 4d sub-shell is in the process of completion of these d-block elements.
Period 6
This period contains thirty two 32 elements. This is also called a long period. The elements are from Cs55 to Rn86.
| Cs55 | Ba56 | La57 | Hf72 | Ta73 | W74 | Re75 | Os76 | Ir77 |
| Pt78 | Au79 | Hg80 | Tl81 | Pb82 | Bi83 | Po84 | At85 | Rn86 |
The first two elements are from s-block. Next fourteen elements are from f-block. Next 10 elements are from d-block and last six are from p-block. The last one Rn is a nobel gas.
The 14 elements which are f-block are called rare earths. They are just after La57. Therefore, they are called Lanthanides. They range from Ce58 to Lu71. Their 4f-sub-shell is in the process of completion or filling.
Period 7
This is an incomplete period. At present, it is consisted of 24 elements. The different thing about this period is that all the elements of this period are radioactive. The elements are from Fr87 to element of atomic number 110.
First two elements are s-block. Next 14 elements are f-block and next eight elements are from d-block. There are no p-block and inert gases elements.
| Fr87 | Ra88 | Ac89 | unnilquadium104 | unnilpentium 105 | unnilhexium 106 | unnilseptium 107 | unniloctium 108 | unnilennium 109 |
The 14 elements from th90 to Lr103 are actinides. They are just after Ac89, so they are called actinides. Their 5f sub-shell is in the process of completion.
Transuranic elements
The elements after U92 are called tansuranic elements. They have been prepared by the scientists in the laboratories around the world. Therefore they are also called artificial elements or synthetic elements.
Lanthanides and actinides are placed at the bottom of the periodic table.
Rare earth elements
Lanthanides and actinides are called rare earth elements as they rare on the earth and not found in higher amounts. So they are known to be rare earth elements.
Families in the periodic table
1: Alkali metals
- The elements of the I-A group are also called alkali metals.
- They have only one electron in their outermost s-orbital.
- They have the properties to form strong alkalies with water.
| Group I-A | Li3 | Na11 | K19 | Rb37 | Cs55 | Fr87 |
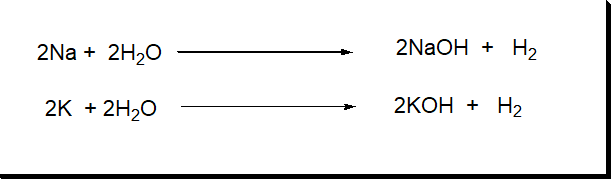
2: Alkaline earth metals
The elements of the II-A group are also known as alkaline earth metals. In their outermost s-orbital, these possess two-electron. These are present in the earth’s crust with alkaline character.
| Group II-A | Be4 | Mg12 | Ca20 | Sr38 | Ba56 | Ra88 |
3: Chalcogens
The elements in this group VI-A are known as Chalcogens. These elements have 6 electrons in their outermost shell. These are electronegative elements.
| Group VI-A | O8 | S16 | Se34 | Te52 | Po84 |
4: Halogens
The elements of group VII-A are called halogens. They possess 7 electrons in the outermost shell. They are electronegative elements.
| Group VII-A | F9 | Cl17 | Br35 | I53 | At85 |
5: Inert gases
The elements of this group VIII-A are called inert gases. It is also called the zero group because these elements are chemically inert due to the complete outermost shells. The elements of this group are also known as Nobel gases.
| Group VIII-A | He2 | Ne10 | Ar18 | Kr36 | Xe54 | Rn86 |
Blocks in the modern periodic table
Elements can be divided into four sections or blocks in the long form of periodic table. For this division, we should take in view of the outermost orbital. Their orbital may not always belong to the outermost shell. There are four blocks in the modern periodic table.
(i) s-block (ii) p-block
(iii) d-block (iv) f-block
These blocks have been named on the basis of outermost electron going to enter in any of s, p , d, pr f sub-shell.
Let us discuss in detail…
S block elements
The elements of groups IA and IIA along with He gas are included in the s-block. Their valance shell configuration is ns1 and ns2. Here n is the number of periods in which the element is lying. These are called normal elements or representative elements.
| I-A | |
| H1 | II-A |
| Li3 | B2 |
| Na11 | Mg12 |
| K19 | Ca20 |
| Rb37 | Sr38 |
| Cs55 | Ba56 |
| Fr87 | Ra88 |
P block elements
The elements of IIIA, IVA, VA, VIA, VIIA, and VIII(O) groups are included in the p-block elements. Their outermost electronic configuration is ns2, np1 to ns2, np6.
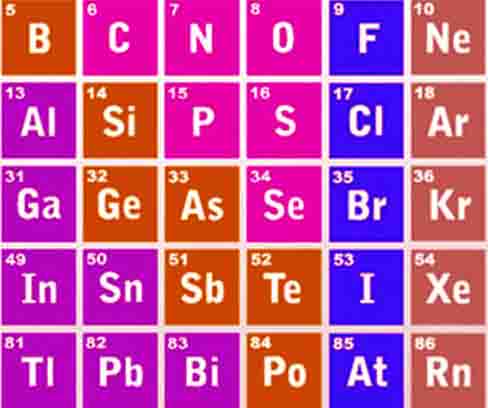
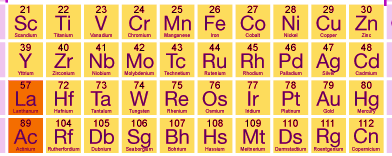
d-block elements
The elements of the periodic table in which the last electron enters in the d-orbital of the penultimate shell are called d- block elements. penultimate refers to inner to outermost. In other words, the last electron goes to (n -1) d-orbital. There are four series of d-block elements as shown in the following table.
f-block elements
Those elements of the periodic table in which the last electron enters in the f-orbital of the anti-penultimate shell. Anti-penultimate means inner to the penultimate. These series are called lanthanides and actinides. They are present in the sixth and seventh periods of the periodic table. There are total of 28 elements in this f-block.
Lanthanides
These are fourteen elements from Cs58 to Lu71. They are present in the sixth period of the periodic table. They are placed below the periodic table. These are called Lanthanides because they are just after La57. Their outermost sub-shell 4 is in the process of completion.
| Ce58 | Pr59 | Nd60 | Pm61 | Sm62 | Eu63 | Gd64 |
| Tb65 | Dy66 | Ho67 | Er68 | Tm69 | Yb70 | LU71 |
Actinides
There are 14 elements from Th90 to Lr103. These are present in the seventh period of the periodic table. They are placed below the periodic table. These are called actinides because they are just after Ac89. Their outermost sub-shell 5f is in the process of completion.
| Th90 | Pa91 | U92 | Np93 | Pu94 | Am95 | Cm96 |
| Bk97 | Cf98 | Es99 | Fm100 | Md101 | No102 | Lw103 |
Metals, Non-metals, and Metalloids in the modern periodic table
Elements of the periodic table can be categorized into another way. This way is based upon the way of reactivity of these elements.
There are three types in this category.
(a) Metals
Elements of group I-A and II-A are good metals. Because these have larger atomic sizes and loosely attached outermost electrons. Moreover, d and f-block elements are also metals by nature.
General properties of the metals.
The elements which have tendency to form positive ion by losing electrons are called metals.
- These are good conductors of heat.
- These are good conductors of electricity.
- These are malleable and ductile.
- They form basic oxides and produce bases with water.

(b) Non-metals
Non-metals are present on the top right of the periodic table.
General properties of Non-metals
The elements which have tendency to form negative ions by gaining electrons are known as non-metals.
- These are not mostly good conductors of heat and electricity.
- They form acidic oxides and give acids when dissolved into the water.
(c) Metalloids
Some of the elements of the periodic table, especially lower members of groups III-A, IV-A, and V-A have the properties of both metals and non-metals.
General properties of metalloids
- Their electron losing and gaining ability is somehow intermediate between metals and non-metals.
- Their electrical and thermal conductivities are also intermediate between metals and non-metals.
- Their oxides are amphoteric, which means that they can act as both acidic and basic oxides both.
The modern periodic table is considered the valid version of the periodic table.
Let others know about this