Drinking acid can have severe and potentially life-threatening consequences. Acids are highly corrosive substances that can cause significant damage to the body’s tissues and organs. The specific effects will depend on the type of acid consumed, its concentration, and the amount ingested.
I am saying this because I witnessed in the laboratory. One of my student used his mouth instead of sucker for acid. Luckily, It was a minor touch of acid that burnt his lips and inner mouth severely. I immediately took him to department’s dispensary.
Remember in this article we are just talking about acids present in chemical labs not natural ones. Even though we cannot take natural acids such as in Lemon in extra amount because it too has consequences.
Here are some general effects of ingesting acids:
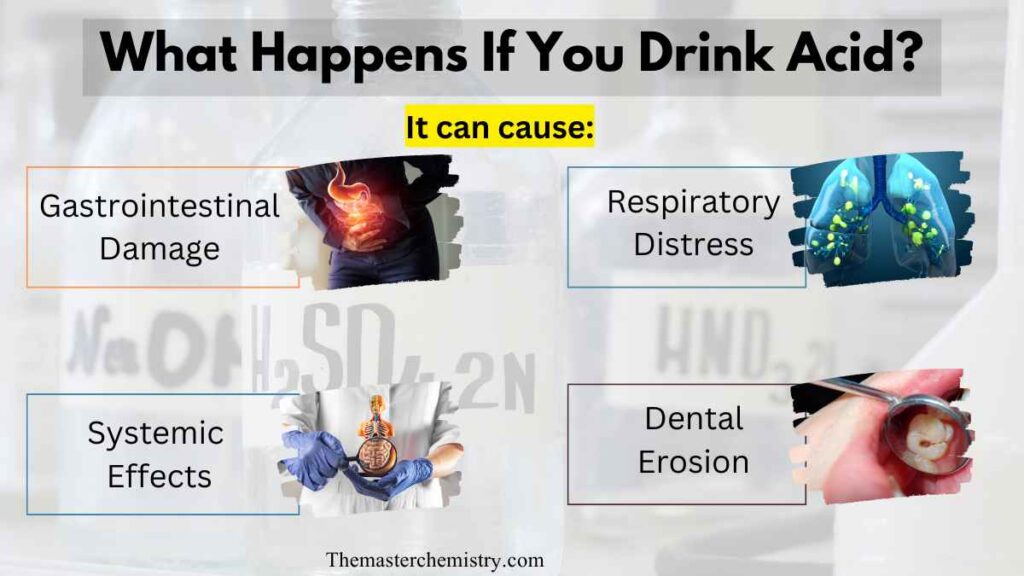
1: Gastrointestinal damage
Table of Contents
Acids can cause severe burns and tissue damage in the mouth, throat, esophagus, and stomach. This can lead to pain, difficulty swallowing, vomiting blood, and potentially life-threatening complications such as perforation or internal bleeding.
2: Respiratory distress
If acid is aspirated into the lungs during ingestion or vomiting, it can cause inflammation, chemical pneumonitis (lung inflammation), or even respiratory failure. This can result in coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, and a bluish discoloration of the skin.
3: Systemic effects
Depending on the type and concentration of acid, it can be absorbed into the bloodstream and affect other organs. This can lead to systemic toxicity, electrolyte imbalances, organ damage, and metabolic disturbances.
4: Dental erosion
Acidic substances can also cause erosion of tooth enamel, leading to dental problems such as tooth sensitivity, discoloration, and increased risk of cavities.
It is crucial to note that ingesting acids is extremely dangerous, and immediate medical attention is necessary. If someone accidentally ingests acid or shows any symptoms after ingestion, contact emergency services or a poison control center immediately.
How to prevent it?
Prevention is key to avoiding such incidents. Proper storage of acids, education about the dangers of ingestion, and ensuring the availability of safety protocols and emergency response measures can help reduce the risk of accidental acid ingestion.
Remember, the information provided here is general, and the effects can vary depending on the specific acid involved. It is always best to consult medical professionals or poison control centers for accurate and timely guidance in case of emergencies.