Introduction
Table of Contents
Autoclaves are essential devices in various fields, including healthcare, laboratories, and industrial settings, where sterilization is crucial. These powerful machines use steam and pressure to eliminate microorganisms, ensuring the safety and cleanliness of equipment and materials. In this article, we will explore the working principle, components, types, applications, and benefits of autoclaves.

I. Understanding Autoclaves
An autoclave is a sealed chamber that utilizes high temperature, pressure, and steam to achieve sterilization. It effectively destroys bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that can cause contamination and infection.
II. Working Principle of Autoclaves
Autoclaves operate based on the principle of moist heat sterilization. The process involves the following steps:
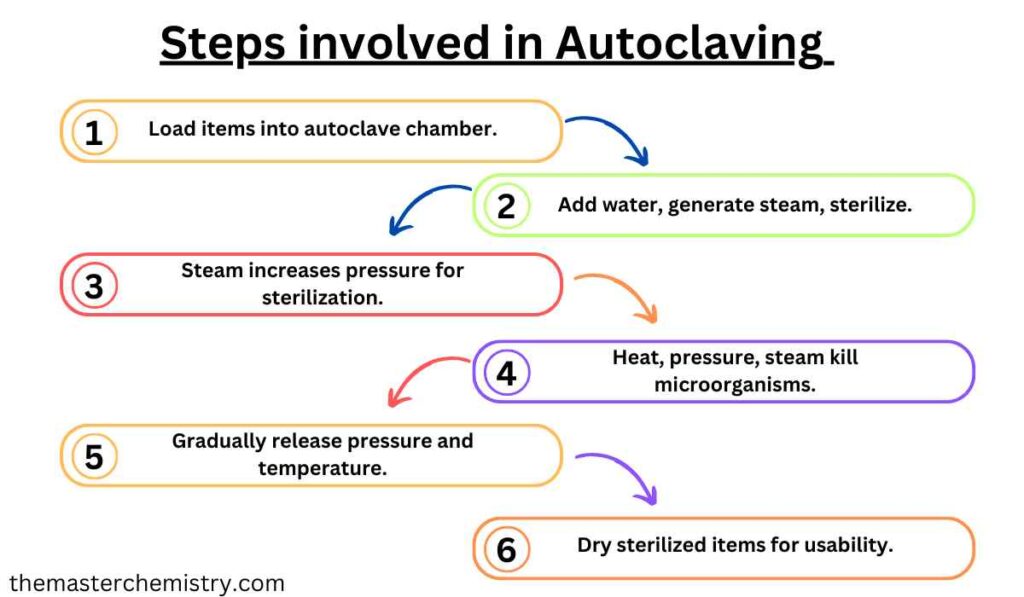
1. Loading
The items to be sterilized are placed inside the autoclave chamber. These may include medical instruments, laboratory glassware, surgical supplies, and other heat-resistant materials.
2. Steam Generation
Water is added to the autoclave, which then generates steam. The steam rapidly fills the chamber, creating a high-temperature environment.
3. Pressurization
As the chamber fills with steam, the pressure inside increases. Autoclaves typically operate at pressures ranging from 15 to 30 pounds per square inch (psi), depending on the specific application and requirements.
4. Sterilization
The combination of high temperature and pressure ensures efficient sterilization. The steam penetrates the items, effectively killing microorganisms by denaturing their proteins and destroying their cell structures.
5. Depressurization
After the sterilization cycle, the autoclave gradually releases the pressure and reduces the temperature. This process is done carefully to prevent sudden changes that could damage the sterilized items.
6. Drying
Some autoclaves include a drying phase where the residual moisture is removed from the sterilized items, ensuring they are ready for use or storage.
III. Components of an Autoclave
Autoclaves consist of several key components:

1. Chamber
The autoclave chamber is a robust, sealed container that holds the items to be sterilized. It is designed to withstand high pressure and temperature.
2. Door and Locking Mechanism
The door of the autoclave securely seals the chamber during the sterilization process. It includes a locking mechanism to prevent accidental openings while under pressure.
3. Control Panel
The control panel allows users to set the sterilization parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and cycle duration. It also displays real-time information and alerts about the progress of the sterilization process.
4. Pressure and Temperature Sensors
Autoclaves are equipped with sensors that monitor and regulate the pressure and temperature inside the chamber. These sensors ensure safe and accurate sterilization cycles.
5. Safety Features
To ensure user safety, autoclaves include various safety features, such as pressure relief valves, overheat protection, and door interlocks that prevent opening while the chamber is pressurized.
IV. Types of Autoclaves
Autoclaves come in different types to cater to specific needs:
1. Steam Autoclaves
Steam autoclaves are the most common type and are widely used in healthcare and laboratory settings. They use saturated steam for sterilization.
2. Vacuum Autoclaves
Vacuum autoclaves are designed to remove air and create a vacuum within the chamber before introducing steam. They are suitable for sterilizing materials that are sensitive to heat and moisture.
3. Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Autoclaves
Ethylene oxide autoclaves use a gas called ethylene oxide for sterilization. They are used for materials that cannot withstand high heat or moisture, such as certain plastics and electronics.
4. Dry Heat Autoclaves
Dry heat autoclaves employ high temperatures without steam for sterilization. They are used for materials that are sensitive to moisture or cannot withstand exposure to steam.
V. Applications of Autoclaves
Autoclaves have numerous applications across various industries:
1. Healthcare
In healthcare facilities, autoclaves are essential for sterilizing surgical instruments, medical devices, and supplies. They help prevent infections and ensure patient safety.
2. Laboratories
Laboratories utilize autoclaves for sterilizing laboratory glassware, media, culture samples, and waste materials. They play a crucial role in maintaining a sterile and safe laboratory environment.
3. Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, autoclaves are used for sterilizing equipment, containers, and pharmaceutical products to ensure product safety and regulatory compliance.
4. Food Industry
Autoclaves find applications in the food industry for sterilizing packaging materials, utensils, and food containers to prevent spoilage and contamination.
5. Research and Biotechnology
Research laboratories and biotechnology companies rely on autoclaves for sterilizing culture media, lab equipment, and biohazardous waste.
Benefits Of Autoclave
The benefits of using autoclaves include:
Effective sterilization
Autoclaves provide reliable and efficient sterilization, eliminating a wide range of microorganisms.
Versatility
Autoclaves can sterilize various materials, including heat-resistant items, liquids, and waste.
Safety assurance
Autoclaves offer safety features and precise control over sterilization parameters, ensuring the safety of both users and the environment.
Time and cost efficiency
Autoclaves provide rapid sterilization cycles, saving time and resources compared to other sterilization methods.
Autoclaves have revolutionized sterilization processes, enabling the safe and efficient elimination of microorganisms. By understanding their working principle, components, types, applications, and benefits, we can appreciate the vital role they play in healthcare, laboratories, and other industries. Autoclaves provide a simple yet powerful solution to ensure the cleanliness, safety, and reliability of equipment, materials, and products.