Chapter 2: S-block elements
In this article, the author has explained the most important chemistry MCQs from the second chapter( S-block elements ) of FSC 2nd year chemistry. All the correct answers have been bold.
1: All of these can react with ice even at -100oC except
- Ca
- K
- Rb
- Cs
2: The pair of elements that have similar chemical properties is
- Beryllium
- Carbon and nitrogen
- Lithium and Magnesium
- Aluminum and Magnesium
3: As the alkaline earth metals (except Be) tend to lose their valence electrons readily, they act as
- Bases
- Strong reducing agents
- Weak oxidizing agents
- Weak reducing agents
Related: FSC 2nd year chemistry 1st chapter MCQs-Periodic classification of elements and periodicity Mcqs
4: KO2 is an example of
- Normal oxide
- Sub oxide
- Super oxide
- Peroxide
5: Elements of group 14
- From M4– and M4+ ions
- Exhibit oxidation state of +4
- Form M4+ ions
- Exhibit oxidation state of +4 and +2
6: All of the followings always act as bases except
- MgO
- BeO
- Na2O
- BaO
7: Noble gases are a group of elements which exhibit very
- High chemical activity
- High electronegativity
- Less diamagnetic property
- Low chemical activity
8: Which of the following is arranged in order of increasing thermal stability?
- BaCO3 < SrCO3 < CaCO3 < MgCO3
- MgCO3 < CaCO3 < SrCO3 < BaCO3
- CaCO3 < MgCO3 < BaCO3 < SrCO3
- MgCO3 < CaCO3 < SrCO3 < BaCO3
- MgCO3 < SrCO3 < CaCo3 < BaCO3
9: Which one of the following is correct about stability of the given ions?
- Sn4+ > Sn2+
- Pb2+ > Pb4+
- Pb4+ > Pb2+
- Si2+ > Si4+
10: N forms NCl3 whereas P can farm bath PCl3 and PCl5 why?
- N atoms are larger than P atoms in size
- P is more reactive towards Cl than N
- P has low lying 3d orbitals, which can be used for banding but N does not 3d orbitals in its valence shell
- None of these
11: Which one of the following statements regarding helium is correct?
- It is used in gas-cooled nuclear reactors
- It is used to produce and sustain powerful super conducting magnets
- It is used as a cryogenic agent for carrying out experiments at low temperatures
- All are correct
12: In case of the oxygen family (group 16)
- The tendency for catenation decreases markedly as we go down the group
- Maximum coordination of oxygen is four due to lack of d orbital, but that of other elements is six due to presence of d orbitals
- The tendency to form multiple bands with C, N and O decreases as going down the group from s to Te
- All are correct
13: Which of the following is arranged in order of increasing melting point?
- Be < Ca < Sr < Mg
- Sr < Mg < Be < Ca
- Ca < Be < Mg < Sr
- Mg < Sr < Ca < Be
14: Alkali metals are characterized by
- Good conductor of heat and electricity
- High oxidation potentials
- High melting point
- Solubility in liquid ammonia
- 1,2
- 1,2,4
- 2,3,4
- All of these
15: The solubilities of carbonates decrease down the magnesium group due to the decrease in
- Hydration energies of cations
- Lattice energies of solids
- Inter ionic interaction
- Entropy of solution formation
16: Following statements regarding the periodic table trends of chemical reactivity of the alkali metals and the halogens are given. Which one of these statements gives the correct picture?
- The reactivity decrease in the alkali metals but increases in the halogens with increase in atomic number down the group
- In both the alkali metals and the halogens the chemical reactivity decreases with increase in atomic number down the group
- Chemical reactivity increases with increase in atomic number down the group in both the alkali metals and halogens
- In alkali metals the reactivity increases but in the halogens it decreases with increase in atomic number down the group
17: Based on lattice energy and other considerations which one of the following alkali metal chlorides is expected to have the highest melting point?
- LiCl
- KCl
- NaCl
- RbCl
18: the graph represents the variation of a property of the group II elements
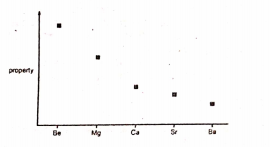
What is this property?
- Ionic radius
- Neutron / proton ratio
- Ionization energy
- Rate of reaction with water
19: The products of decomposition of Mg(NO2)2 are
- MgO and NO2
- MgO, NO2 and O2
- Mg and NO2
- Mg(NO2)2
20: Which salts of alkali and alkaline earth metals do not decompose on heating?
- Halides
- Bicarbonates
- Nitrates
- None of these
21: A solution of Na in liquid NH3, serves as a good reducing agent due to the reaction;
- 2Na + 2NH3 —> 2NaNH2 + H2
- 2Na + 2H2O —> 2NaOH + H2
- NaNH2 + N2O —> NaN3 + H2O
- None of these
22: A white solid (sodium salt) on heating liberates a gas and leaves an alkaline residue. The gas turns lime water milky. The solid is
- Na2CO2
- NaHCO2
- NaHSO4
- NaNH4HPO4
23: Magnesium is present in
- Ascorbic acid
- Chlorophyll
- Vitamin B12
- Hemoglobin
24: Pick out the incorrect statements about noble gases
- He cannot be used in preference to nitrogen to dilute the oxygen in the gas cylinders used by divers
- Helium is used in weather balloons and airships
- Helium is used in cryoscopy to obtain the very low temperatures required for superconductivity and lasers
- Ar is used in metallurgical process
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 4
- 1 only
25: The calcium salt used as a fertilizer is
- CaC2
- CaCO2
- CaCN2
- CaSO4
26: The oxide that can never act as a reducing agent is
- SO2
- CO
- CO2
- NO2
27: The purest form of silica is
- Quartz
- Sand
- Flint
- Kieseiguhr
28: Chlorine acts as a bleaching agent in the presence of
- Dry ice
- Moisture
- Sunlight
- Pure oxygen
29: An element of group VIIA which does not show oxidation state equal to the group number is
- F
- Cl
- Br
- I
30: Which of the following statement is true for the halogen hydrides, HF, HCl, HBr, HI?
- All form intermolecular H-bonds with water in aqueous solution
- Bond length is greatest in HF
- HF cannot be oxidized to F2 by any of the other halogens
- An aqueous solution of HF is the strongest acid
31: The strongest reducing agent amongst the followings is
- HF
- HCl
- HBr
- HI
32: In silicon dioxide
- There are double bonds between silicon and oxygen atoms
- Silicon is bonded to two silicon atoms
- Each silicon atom is surrounded by two oxygen atoms and each oxygen atom is bonded to two silicon atoms
- Each silicon atom is surrounded by four oxygen atoms and each oxygen atom is bounded to two silicon atoms
33: In the use of chlorine as bleaching agent, the substance that is mainly responsible is
- HOCl
- CL2
- HCl
- None of these
34: Excess Cl2, during bleaching is removed by reaction with antichlor which is
- Na2S
- Na2SO3
- Na2SO4
- Na2S2O3
35: When chlorine water is exposed to sunlight, O2 is liberated: Hence
- Hydrogen has little affinity to O2
- Hydrogen has no affinity to O2
- Hydrogen has more affinity to chlorine
- It is a reducing agent
36: The halide which fails to give a precipitate with AgNO3 is
- F–
- Cl–
- Br–
- I–
37: If CO2 is passed in excess through lime water, the milkiness first formed disappears due to
- The solution getting heated by exothermic reaction
- Formation of water soluble calcium bicarbonate
- Reversal of the original reaction
- Formation of volatile calcium derivative
38: Silica is soluble in
- HF
- HNO3
- H2SO4
- HCl
39: One can obtain a silica garden if
- Silicon salts are grown in garden
- Crystals of colored cations are added to a strong solution of sodium silicate
- Silicon tetrafluoride is hydrolyzed
- Sodium silicate solution is heated with a base
40: Which of the following is most vaporizing?
- HI
- HCl
- HBr
- HF
41: Which of the following statements is false?
- He2 does not exist
- Radon is obtained from the decay of radium
- The most abundant rare gas found in the atmosphere is helium
- Xenon is the most reactive among the rare gases
42: Identify the incorrect statement among the following:
- Cl2 reacts with excess of NH3 to give N2 and HCl
- Silicon reacts with NaOH(aq) in the presence of air to give Na2SiO3 and H2O
- Br2 reacts with hot and strong NaOH solution to give NaBr, NaBrO4 and H2O
- Ozone reacts with SO2 to give SO3
43: Which of the following oxides is amphoteric in character?
- CO2
- SiO2
- SnO2
- CaO
44: Bleaching powder loses its available chlorine on standing because
- It changes into calcium hypochlorite and calcium carbonate
- It changes into calcium bicarbonate and chlorine
- It changes into calcium chlorate and calcium chloride
- It changes into calcium chlorate and calcium carbonate
45: What are the products formed when Li2CO3 undergoes decomposition?
- LiO2 + CO
- Li2O + CO
- Li2O + CO
- Li2O + CO2
46: Sodium sulfate is soluble in water but barium sulfate is sparingly soluble because
- The lattice energy of barium sulfate is more than its hydration energy
- The hydration energy of sodium sulfate is more than its lattice energy
- The lattice energy has no role to play in solubility
- The hydration energy of sodium sulfate is less than its lattice energy
47: In the manufacture of metallic sodium by the fused salt electrolysis (Down’s Process) a small amount of calcium chloride is added to
- Improve the electrical conduction
- Bring down the melt temperature
- Increase the temperature of electrolysis
- Stabilizes the metallic sodium
48: Plaster of Paris has the formula
- CaSO4. 2H2O
- (CaSO4)2 . H2O
- CaSO4.H2O
- (MgSO4)2.H2O