LEARNING OBJECTIVES
In this article, the author has explained basic concepts of chemistry. This article covers the topic such as elements, relative atomic mass unity.
Basic concepts in chemistry-Atom, Elements, relative atomic mass unit
Table of Contents
Chemistry is considered to be a boring subject. This consideration makes chemistry more difficult to understand. The basic concepts in chemistry can help us understand it in a more efficient way. Similarly, if we ignore the basic concepts in chemistry it’s like a tough challenge.
Below given is the list of some basic concepts in chemistry to let you go through chemistry.
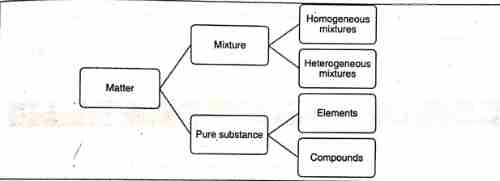
Matter
Any species having mass and occupies space is known as matter.
Characteristics of elements
- An element is a pure substance made up of only one kind of atoms (Na, Fe, etc) or molecules(H2, Cl2, etc).
- An atom is the smallest unit of an element and it processes the properties of that element
- Elements that may occur in the free state in nature are found in the form of their compounds
- The properties of different elements are different. This is because the arrangement of electrons (electronic configuration) in atoms is different.
Atom
The smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction
Atom may or may not exist independently. ( monatomic gas is like helium, Neon can exist independently and, Fe, oxygen at 17 cannot exist independently).
Evidence of Atoms cannot be observed by
Naked eye optical microscope
Atoms can be observed with the nearest possibility by
Electron microscope, x-ray diffraction analysis
Atom is made up of more than a hundred particles divided into two types.
Fundamental particles
Electron, proton, and neutron
Subatomic particles
It includes all types of particles including electron proton neutron Meson etc.
The largest atom with respect to size is cesium and the smallest atom is helium in the periodic table.
The most abundant type of atom in the universe is the hydrogen atom and the second most abundant atom is helium.
The diameter of an atom is around 0.2 nm.
Mass of an atom ranges10-27 to 10-25 kg.
Atoms of the same element may also differ in mass and mass-related properties in the case of isotopes.
Relative atomic mass
Relative mass is the mass of an atom of an element as compared to the mass of an atom of carbon taken as 12.
C-12 is used as standard in this scale because its mass is exactly in whole number i.e 12.0000.
Atomic mass unit
The unit used to express the relative atomic mass is called atomic mass unit (amu) and it is 1/12 is of the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
1 amu = 1.66 × 10-27 kg
Examples
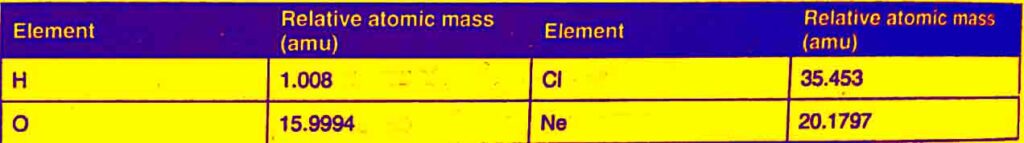
Calculations of Average atomic masses using relative atomic masses of isotopes

Relative isotopic mass
Relative isotopic mass is the mass of an atom of an isotope compared with the one-twelfth 1/12 mass of a carob-12 atom.
Examples
i) Relative isotopic mass of Chlorine Cl35 is 35 amu.
ii) Relative isotopic mass of Chlorine Cl37 is 37 amu.
Relative Molecular mass
Relative molecular mass of a compound us defined as the mass of a formula unit of the compound relative to the mass of a carbon atom taken as exactly 12.
Examples
i) Relative molecular mass of water (H2O) is 18 amu
ii) Relative molecular mass of Carbon dioxide (CO2) is 44 amu
Relative formula mass
The relative formula mass of an ionic compound can be defined as the mass of a formula unit of the compound relative to the mass of a carbon atom taken as exactly 12.
Examples
i) Relative formula mass of MgO is 40 amu
ii) Relative formula mass of NaCl is 58.5 amu
Related questions
1: What is the atomic mass unit?
It is a unit of mass used for atoms and molecules that is equal to the 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12/ It is obtained by dividing the unity by Avogadro’s number 6.02 x 10-24.
As one a.m.u is equal to 1.6603 x 10-27 kg = 1.6603 x 10-24 g.
2: What are molecular ions?
Any molecular species bearing a positive or negative charge is known to be a molecular ion. These are mostly produced when a beam of electrons with energy potential between 10 to 15 eV is bombarded on molecules of a compound in the vapor phase. The examples may be CO+, N2+, C2H4+, O2+, CH4+.
3: Why the atomic masses may be in fractions?
The majority of the elements have isotopes in the modern periodic table with their respective atomic masses. Therefore, when we talk about average atomic masses of isotopes will be in fractions. However, talking about monoisotopic elements, these also have fractional atomic masses.