Written by Adeel Abbas
This is a covalent bond in which the electron cloud overlap is directly between the nuclei of the atoms involved in the bonding.
Characteristic of sigma bond
Table of Contents
- A sigma bond will be formed using electrons in s orbitals, p orbitals or hybrid orbitals.
- A sigma bond will always be a single bond.
- A sigma bond is always formed on the nuclear axis between two atoms.
Examples of sigma bond
Sigma bond in Hydrogen
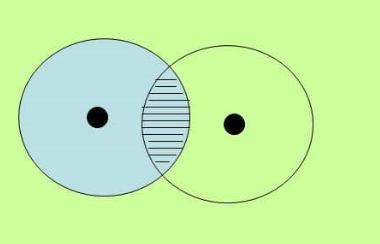
This molecule has the two hydrogen atoms having 1 electron in an s orbitals. Remember that the s orbital is spherical.
In the following diagram, the atoms on the right has been made clear to show the cloud overlap.
Also not how the overlap of the two atom’s clouds is directly between the nuclei of the atoms.
Therefore, the bond in this example is characterized as a sigma bond.
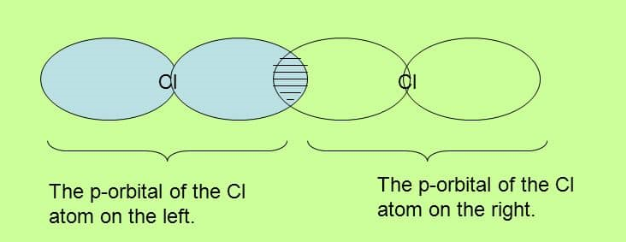
Sigma bond in Chlorine
In chlorine the valence is 7 so that the bond between the atoms is formed by the overlap of p orbitals. Remember also that the shape of a p orbital is like figure 8.
Note again how the overlap is directly between the nuclei of the two atoms.
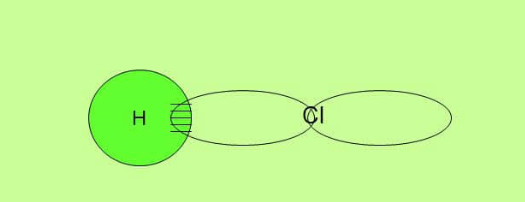
Sigma bond in Hydrochloric acid HCl
In HCl the hydrogen atom has a bonding electron in an s orbital and the chlorine atom has its unpaired electron in a p-orbital.
Again the overlap is directly between the two nuclei. This is characterized as sigma bond.
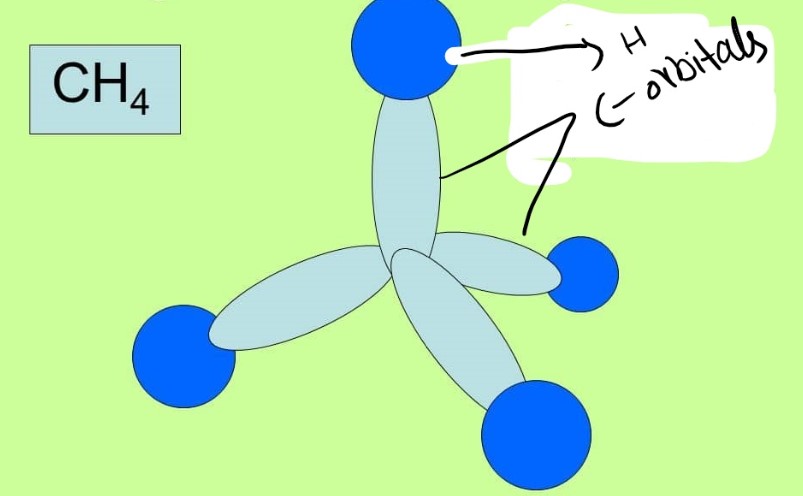
Sigma bond in Methane CH4
In methane there are 4 hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atom. It is to observe that the carbon atom is in SP3 hybridization and is showing a tetrahedral geometry. There are total of 4 bonds but each is a sigma bond as it can be seen in following figure.