Learning Objectives
In this article, you will learn about absolute zero with graphical explanation, scales of thermometry such as centigrade, Fahrenheit, and Celsius, and their interconversions formulas by professional author.
What is absolute zero?
Table of Contents
The hypothetical temperature at which the volume of all gases becomes zero is called absolute zero.
Definition of absolute zero
Its value is -276.16 oC = 0 K
For routine calculations, the value of absolute zero is taken as -273 oC.
Quantitative statement of Charles’s law
At constant pressure the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas increases or decreases by 1/273 of its original volume at 0oC for every 1oC rise or fall in temperature respectively.
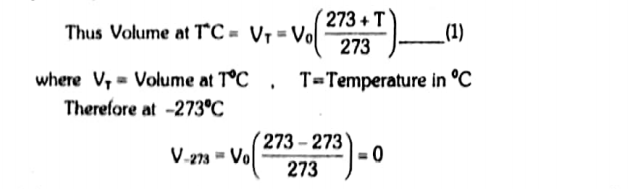
The temperature -373 oC is called absolute zero of the Kelvin scale. Thus the volume of a gas becomes zero at absolute zero.
Absolute zero can never be achieved. It is considered the lowest temperature. Its value is independent of the nature of the gas.
Charles’s law is not obeyed when the temperature is on a centigrade scale. For this reason, the Kelvin scale was developed with 0 K = -273 oC.
Graphical explanation of absolute zero
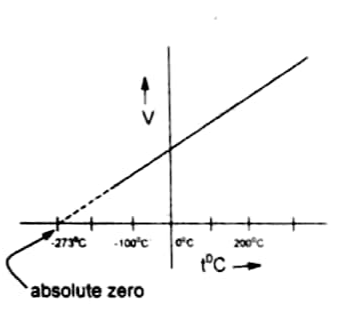
According to Charles’s law when a graph is plotted between V and T for a gas a straight line is obtained.
- This line intersects the temperature axis at -273 oC which is considered the lowest temperature.
- This temperature is achieved if the substance remains in the gaseous form. But all gases liquefy before reaching this temperature.
- Thus, the lines of all the gases are extrapolated. They meet the T axis at -273 at which the volume of all gases becomes zero. However, it can never happen for a real gas. Thus, -273 oC is taken as zero of the Kelvin scale and it is called absolute zero.
- Generally, the greater the mass of the gas greater will be the slope of the line. It is because a greater number of moles of gas occupies more volume.
Scale of thermometry
The branch of science which deals with the measurement of temperature is called thermometry.
Definition of thermometry
There are three measuring scales of thermometry.
1: Centrigrade or Celsius scale (oC)
The temperature measured on this scales is represented by oC.
On this scale freezing point of water is marked as 0oC and boiling point as 100 oC. The distance between these two ends is divided into 100 equal parts. Each part is equal to 1 oC.
2: Fahrenheit scale (oF)
The temperature measured on this scale is represented by oF.
On this scale the freezing point of water is marked as 32 oF and boiling point as 212 oF. The distance between these two ends is divided into 180 equal parts. Each part is equal to 1 oF.
3: Kelvin scale (K)
The temperature measured on this scale is represented by K.
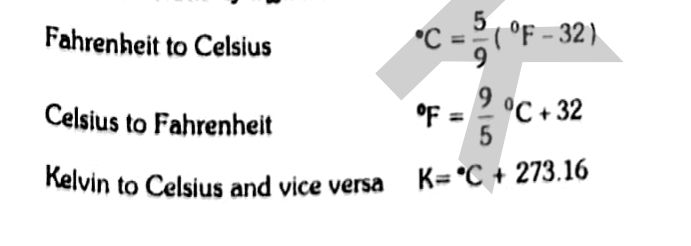
Interconversions of different scales of thermometry
Suggested readings
Thermometers and Temperature Scales