Written by Adeel Abbas
Calorimeters is an important chemistry lab instrument devices that measure the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction. In this article, we will explore the definition of calorimeters in chemistry, their importance, types, and applications.
Definition of Calorimeter in Chemistry
Table of Contents
Calorimeters are instruments that are used to measure the heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction.
They are designed to maintain a constant temperature throughout the reaction, which is achieved through the use of an insulated container. The heat is then transferred to a temperature sensor, which is used to measure the change in temperature.
Calorimeter diagram
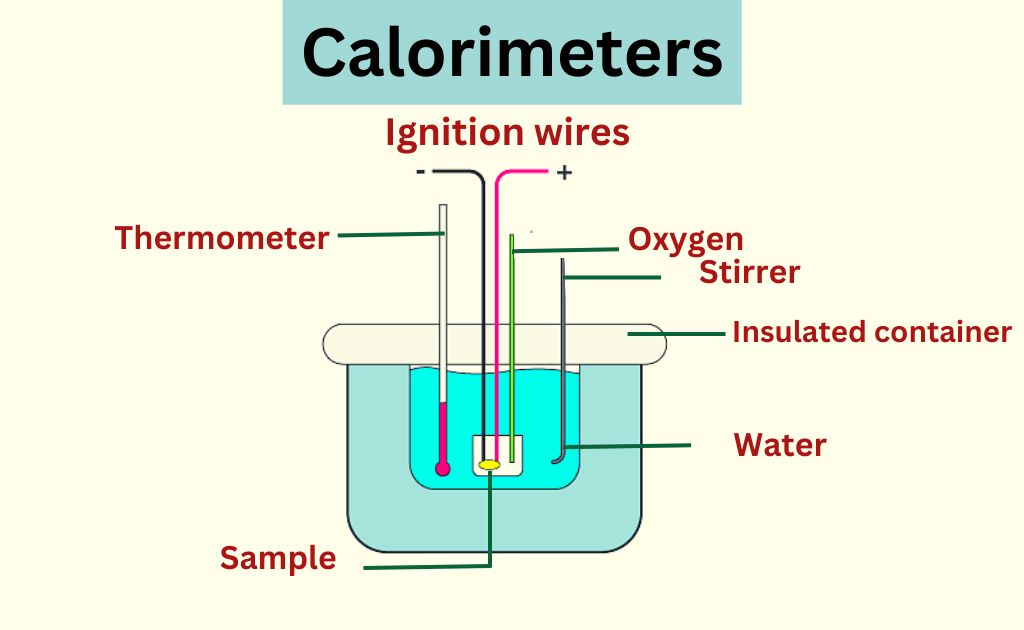
Principle of a calorimeter
The principle of a calorimeter is based on the concept of heat transfer. Calorimetry is the measurement of the heat involved in a chemical reaction or physical change of state. The amount of heat released or absorbed during a reaction is determined by measuring the change in temperature of the surrounding environment. Calorimeters are used to measure the heat of combustion, heat capacity, and heats of reaction.
Importance of Calorimeters in Chemistry
Calorimeters play a crucial role in understanding the thermodynamics of a chemical reaction. They allow scientists to determine the amount of heat energy involved in a reaction, which can help in the design and optimization of chemical processes. Additionally, calorimeters are used to measure the heat of formation, combustion, and other important thermochemical properties of substances.
Types of Calorimeters
There are several types of calorimeters, each with its own advantages and limitations. The most commonly used calorimeters are:
- Bomb Calorimeter– Bomb calorimeters are used to measure the heat of combustion of a substance. The sample is burned in a pressurized oxygen atmosphere, and the heat released is measured.
- Differential Scanning Calorimeter– Differential scanning calorimeters are used to measure the heat of transition of a substance. They are particularly useful in the study of polymers, where they can measure the glass transition temperature and the melting point.
- Isothermal Calorimeter– Isothermal calorimeters are used to measure the heat of reaction at a constant temperature. They are particularly useful in the study of biochemical reactions, where they can measure the heat of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
Instrumentation of calorimeter
The instrumentation of a calorimeter typically includes the following components:
- Insulated Container– The calorimeter is designed to maintain a constant temperature during the reaction, which is achieved through the use of an insulated container. The container is usually made of materials such as Styrofoam or vacuum flasks to prevent heat exchange with the surroundings.
- Temperature Sensor– A temperature sensor is used to measure the change in temperature during the reaction. The most commonly used temperature sensors are thermocouples and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs).
- Stirrer– A stirrer is used to ensure that the reactants are well-mixed and that the temperature is uniform throughout the reaction.
- Heat Source– A heat source is used to initiate the reaction. In some cases, the heat source may be an external source, such as a Bunsen burner or an electric heater. In other cases, the reaction may be initiated by mixing the reactants.
- Data Acquisition System– A data acquisition system is used to record the temperature change during the reaction. The system typically includes a computer, software, and a data acquisition board.
- Calorimetric Vessel– The vessel in which the reaction occurs is typically made of materials such as stainless steel or glass. The vessel may be designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, depending on the type of reaction being studied.
- Cooling System– In some cases, a cooling system may be used to maintain a constant temperature during the reaction. The cooling system typically includes a heat exchanger, a refrigeration unit, and a control valve.
Overall, the instrumentation of a calorimeter is designed to ensure that the temperature remains constant during the reaction and that the heat released or absorbed is accurately measured.
Applications of Calorimeters
Calorimeters have numerous applications in chemistry, including:
- Energy Storage– Calorimeters are used to study the heat of reaction of materials used in energy storage, such as batteries and fuel cells.
- Pharmaceutical Industry– Calorimeters are used to study the heat of reaction of drugs and drug-like molecules, which can help in the design of more effective and efficient drugs.
- Food Industry– Calorimeters are used to study the heat of reaction of food products, which can help in the optimization of food processing and storage.
Calorimeters are essential tools in the study of thermodynamics and the design of chemical processes. They allow scientists to measure the heat of a reaction, which is crucial in understanding the energy changes involved in a chemical reaction. With the right type of calorimeter, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the properties of substances, from polymers to drugs to food products.