Written By Adeel Abbas
Introduction
Table of Contents
Chemistry is a field that relies heavily on laboratory experimentation, and the success of any experiment is largely dependent on the quality of the equipment being used.
From simple tools such as beakers and test tubes to more complex instruments such as spectrophotometers and chromatographs, laboratory apparatuses play a critical role in conducting experiments, making observations, and analyzing data.
In this article, we will explore some of the most commonly used laboratory apparatuses in general chemistry labs, their functions, and how they are used in experiments.
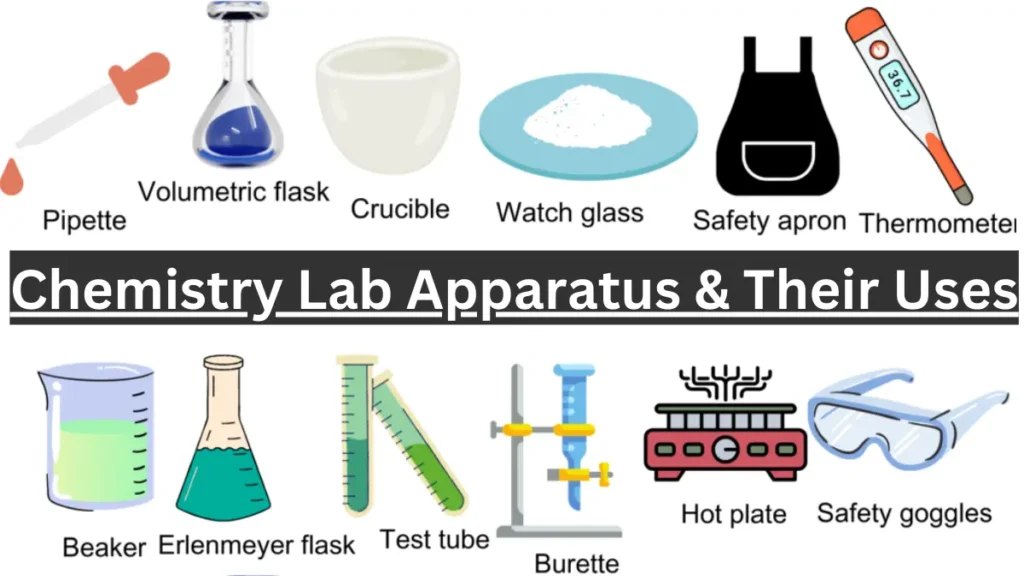
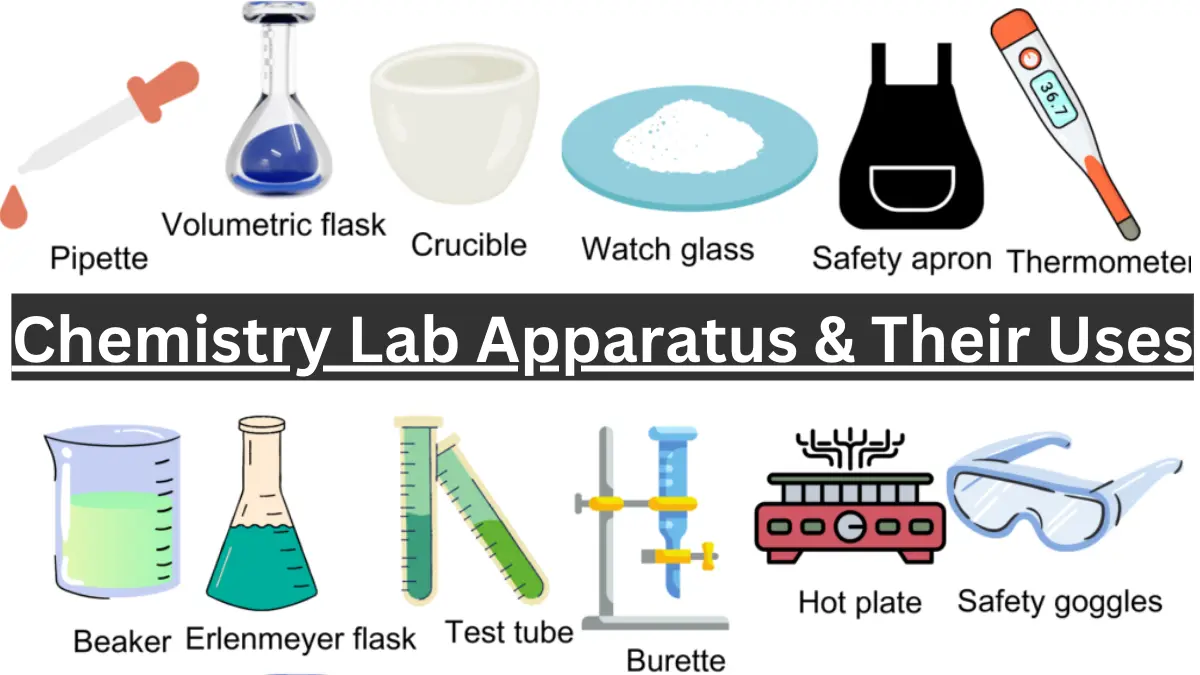
25 laboratory apparatus and their uses
Here are some laboratory apparatus and their uses:
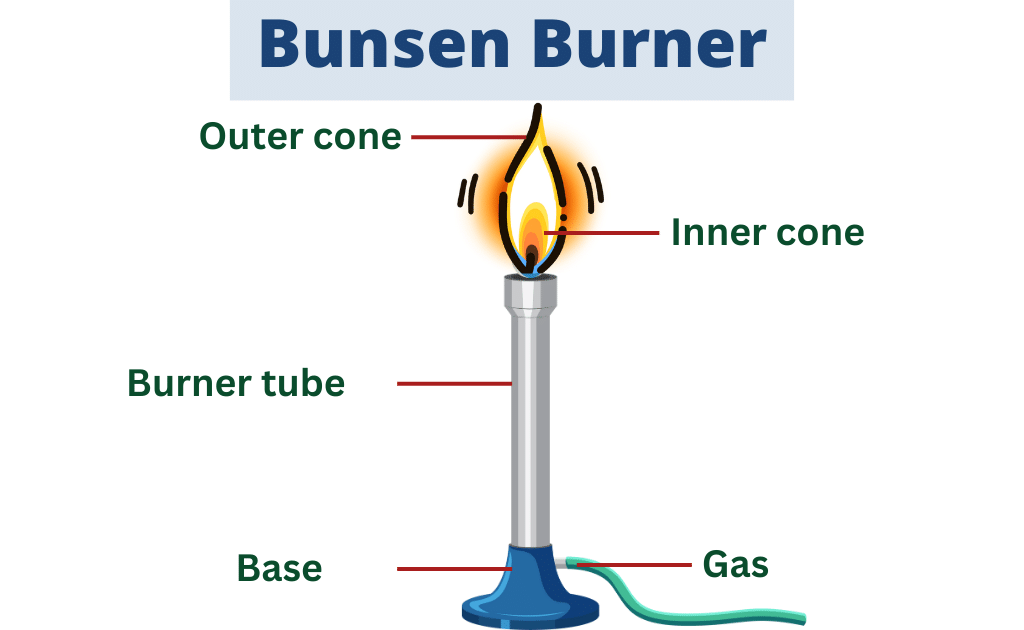
1. Bunsen Burner
A Bunsen burner is a common piece of laboratory equipment that produces a single open gas flame, which is used for heating, sterilizing, and combustion. The burner consists of a metal tube connected to a gas source with adjustable airflow through the tube, which allows control of the flame’s size, shape, and intensity.
2. Erlenmeyer Flask
An Erlenmeyer flask is a conical shaped container with a flat bottom and a cylindrical neck. The narrow neck of the flask helps to prevent the escape of fumes and vapors, while the wide base helps in stability. The flask is used for mixing, heating, and holding liquids.

3. Graduated Cylinder
A graduated cylinder is a common piece of laboratory glassware used to measure the volume of liquids. It has a cylindrical shape with a narrow neck, and it comes in different sizes, from small to large. Graduated cylinders are usually made of glass or plastic, and they have precise measurements marked on their surfaces.

4. Beaker
A beaker is a common piece of laboratory equipment used to hold and mix chemicals. It has a cylindrical shape with a flat bottom and a lip around the rim to aid in pouring. Beakers come in various sizes, and they are usually made of glass, plastic, or stainless steel.

5. Pipette

A pipette is a laboratory tool used to measure and transfer small volumes of liquid. It is a narrow tube made of glass or plastic with a bulbous end. The pipette’s bulb is used to draw liquid up into the tube, and the narrow tip is used to dispense precise amounts of liquid.
6. Pipette Bulb
Pipet bulbs are used to draw and dispense liquids from a variety of pipettes. They are made of a variety of materials, including rubber, latex, and silicone. Pipet bulbs are typically reusable, but they can also be disposable.
Pipet bulbs are used in a variety of laboratory settings, including biology, chemistry, and physics. They are also used in some medical settings, such as when taking blood samples.
7. Thermometer
A thermometer is an instrument used to measure temperature. In the laboratory, thermometers are usually used to measure the temperature of liquids or gases. There are different types of thermometers, including digital and mercury thermometers, and they come in various sizes.

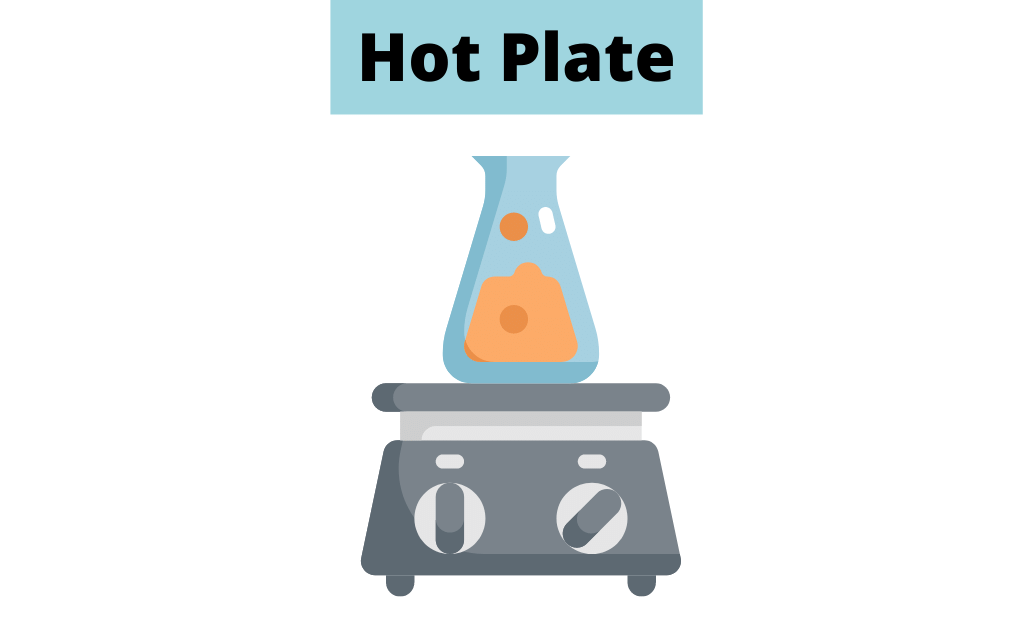
8. Hot Plate
A hot plate is a piece of laboratory equipment that is used to heat substances in the laboratory. It is a flat, electrically powered metal plate that is capable of reaching high temperatures. Hot plates are used to heat liquids, solids, and gases, and they can be used in combination with various types of containers.
9. Test Tubes
Test tubes are cylindrical, thin-walled glass or plastic containers with one open end and one rounded or conical end. They are used to hold, mix, and heat small quantities of liquid or solid samples. Test tubes come in different sizes, and they can be used with a variety of accessories, such as rubber stoppers or test tube racks.
10 Test tube holders
Test tube holders are devices used to hold test tubes in place. They are used in a variety of laboratory settings, including biology, chemistry, and physics, as well as in some medical settings. Test tube holders can be made of a variety of materials, including wood, metal, plastic, and foam.
11. Spectrophotometer
A spectrophotometer is a device used to measure the amount of light absorbed by a sample. It is commonly used in analytical chemistry to measure the concentration of a substance in a solution. The device works by passing light through the sample and measuring the intensity of the light that comes out.

12. Centrifuge
A centrifuge is a machine that is used to separate mixtures of liquids or solids based on their density. It works by spinning a container at a high speed, causing the denser components to move towards the bottom. Centrifuges are commonly used in biological and chemical research to separate and purify samples.

13. pH Meter
A pH meter is an instrument used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. It measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution and provides a numerical value that ranges from 0 to 14. pH meters are commonly used in analytical chemistry and biology to measure the acidity of various samples.

14. Microscope
A microscope is a device used to magnify small objects and view them in detail. It consists of one or more lenses that work together to magnify the object. Microscopes are commonly used in biological and chemical research to view cells and other small structures.

15. Stir Plate
A stir plate is a device used to stir liquids in a laboratory. It consists of a magnetic stir bar that is placed in the liquid and rotated using a magnetic field generated by the stir plate. Stir plates are commonly used in chemical research to mix solutions and create homogenous mixtures.
16. Autoclave
An autoclave is a device used to sterilize laboratory equipment and supplies. It uses high-pressure steam to kill bacteria and other microorganisms on surfaces. Autoclaves are commonly used in microbiology and other biological sciences to ensure that laboratory equipment is free of contamination.

17. Desiccator
A desiccator is a sealed container used to remove moisture from a sample. It is commonly used in analytical chemistry to ensure the accuracy of weight measurements. The desiccator contains a desiccant, such as silica gel or calcium sulfate, which absorbs moisture from the air inside the container.

18. Refractometer
A refractometer is a device used to measure the refractive index of a substance. It works by shining a light through the substance and measuring the angle of refraction. Refractometers are commonly used in analytical chemistry to measure the concentration of a substance in a solution.

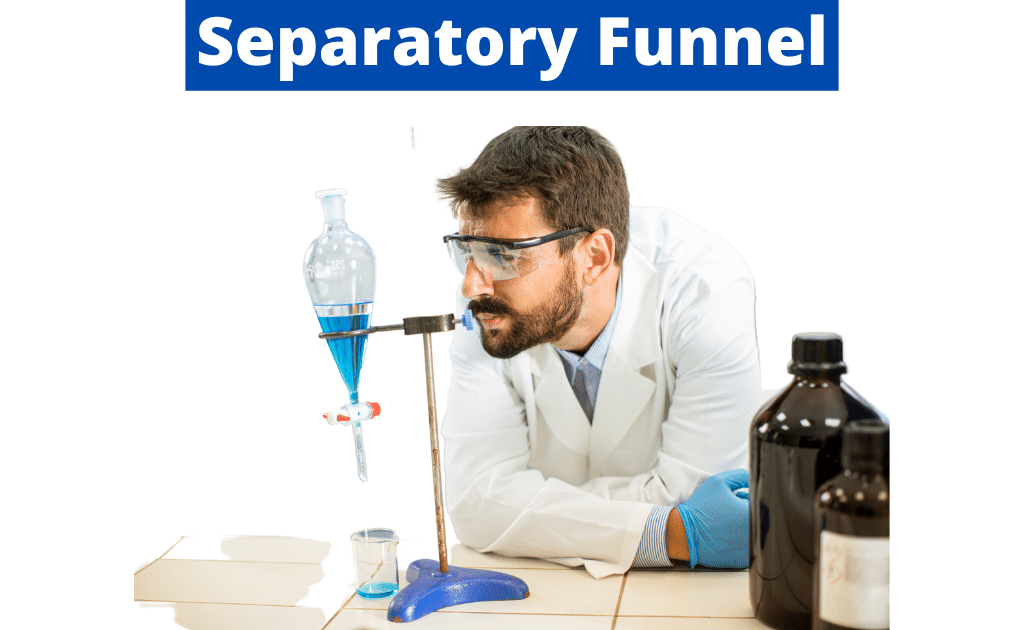
19. Separatory Funnel
A separatory funnel, also known as a separation funnel, is a laboratory apparatus used to separate immiscible liquids. It consists of a funnel with a stopcock valve at the bottom and is used to separate liquids based on their densities. Separatory funnels are commonly used in organic chemistry for extractions and purifications.
20. Conductivity Meter
A conductivity meter is an instrument used to measure the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. It measures the concentration of ions in the solution and provides a numerical value. Conductivity meters are commonly used in analytical chemistry to measure the purity of a substance or the concentration of ions in a solution.
In conclusion, there are many different laboratory apparatuses that are used in general chemistry labs. Each apparatus has a specific purpose and is essential for conducting experiments and procedures. By understanding the uses and functions of laboratory equipment, you can be better equipped to handle them in the lab and conduct successful experiments.
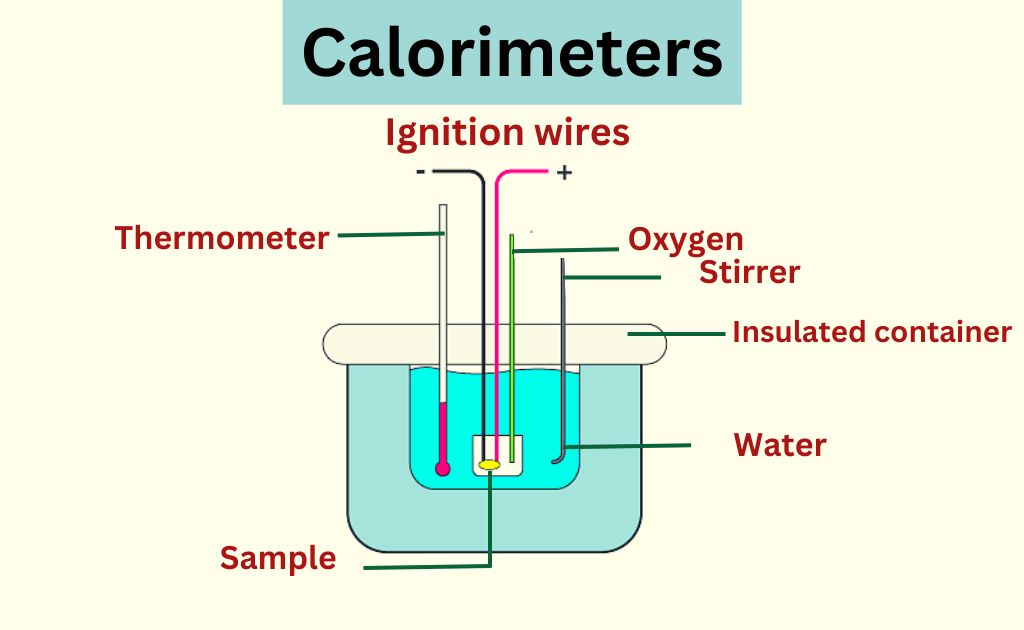
21. Calorimeter
The instrument that are used to measure the heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction is called calorimeter.
22. Spatulas
Spatulas are flat, blade-like tools used to transfer solids from one container to another, or to mix solids. They are typically made of metal, plastic, or glass. Spatulas are used in a variety of laboratory settings, including biology, chemistry, and physics.
23. Spectrophotometers
Spectrophotometers are devices used to measure the amount of light that is absorbed or transmitted by a sample. They are used in a variety of laboratory settings, including biology, chemistry, and physics, as well as in some medical settings.
Spectrophotometers can be used to measure the concentration of a substance in a solution, or to identify a substance based on its absorption spectrum.
24. Wire Gauze
Wire gauze is a mesh made of metal wires. It is used in laboratory settings to support beakers and other glassware during heating. Wire gauze also helps to distribute heat evenly across the bottom of the glassware, which prevents it from cracking.
25. Tongs
Tongs are long-handled tools used to hold and manipulate objects. They are typically made of metal or plastic. Tongs are used in a variety of laboratory settings, including biology, chemistry, and physics. Tongs are used to hold hot objects, such as beakers and test tubes, as well as to hold small objects, such as microscope slides and dissection tools.