LEARNING OBJECTIVES
In this article, the author has explained what is conical flask or Erlenmeyer flask along with its working principle and uses in chemistry laboratory.
What is Conical flask?
Table of Contents
According to Wikipedia, a conical flask is a glass or plastic vessel with a tapering bottom to facilitate the addition and removal of a sample.
It is used as important apparatus in the chemistry lab for a variety of tasks. A conical flask is designed in such a way that a small volume of material can be added to the flask, and later it can be removed through a narrow neck. These flasks are mostly used in the chemical and physical analysis.
The size of the flask is determined by its capacity. A conical flask holds less than 1 mL of liquid and is useful in a wide range of chemical reactions that require very precise measurement.

Conical Flask size
The typical sizes of conical flasks are 6-8 mL, 10 mL, and 15 mL, but they also come in a variety of other sizes, including 25 mL, 50 mL, 100 mL, 125 mL, 150 mL, 250 mL, 300 mL, 500 mL, 1000 mL, 2000 mL, 3000 mL, 4000 mL, 5000 mL, and 6000 mL.
The size of conical flask you choose will depend on the specific application you are using it for. For example, if you are measuring a small amount of liquid, you will need a smaller flask. If you are heating a liquid, you will need a flask that is large enough to accommodate the liquid and any vapor that it produces.
Also read: Separating funnel-Working principle and uses
Discovery of conical or Erlenmeyer flask
Emil Erlenmeyer was a German chemist who discovered the Erlenmeyer flask. He initially specialized in pharmacy, but was eventually drawn back into the world of chemistry, and made many significant contributions to our understanding of the structure of organic molecules.
Conical flask diagram
The Erlenmeyer or Erlenmeyer flask has a broad flat bottom, a conical body, and a high cylindrical neck.
The slanted sides of the Erlenmeyer and the narrow neck allow the contents of the flask to be mixed and swirled without the risk of spilling. There are areas in which Erlenmeyer flasks can be marked or labeled if you pass the test.
How to use a conical flask in a reaction?
There are different ways to use conical flasks, but here are the most common ways:
• Add a sample to the flask.
• Transfer the contents from a larger container into a conical flask.
• Pour a liquid into a conical flask.
• Dilute a solid chemical in a conical flask.
Conical flasks are widely used in the synthesis of organic compounds. The flask is a common method for the dissolution of solid chemicals into solution. It is also used in the synthesis of compounds of interest to the pharmaceutical industry.
Conical flasks are not rinsed with solution because it can dilute the solution being measured or introduce impurities. To rinse conical flasks, use distilled water only. Distilled water is free of impurities and will not dilute the solution being measured.
Rinse the flask multiple times, swirling the water around the flask to coat all of the surfaces. Finally, pour out the water completely.
Principal of Conical Flask
The principle of a conical flask is based on the fact that liquids will flow from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. When a liquid is placed in a conical flask, the liquid will flow down the sides of the flask and collect at the bottom.
The conical shape of the flask helps to concentrate the liquid at the bottom and prevents it from overflowing.
Another important principle of the conical flask is that the surface area of the liquid in the flask is proportional to the volume of the liquid. This means that as the liquid level in the flask increases, the surface area of the liquid also increases.
This increased surface area allows for more heat transfer and evaporation, which can be useful for certain applications.
The basic principle of a conical flask is very similar to a funnel; a thin layer of liquid is collected at the bottom. So, this is the reason why a conical flask is so versatile. You can fill a conical flask with any liquid, and it will easily collect a layer of that liquid at the bottom of the flask.
Uses Of Conical Flasks
Conical flask is multipurpose instrument that is used in chemistry, and Biology labs as well. Here are its few uses in different diciplines:
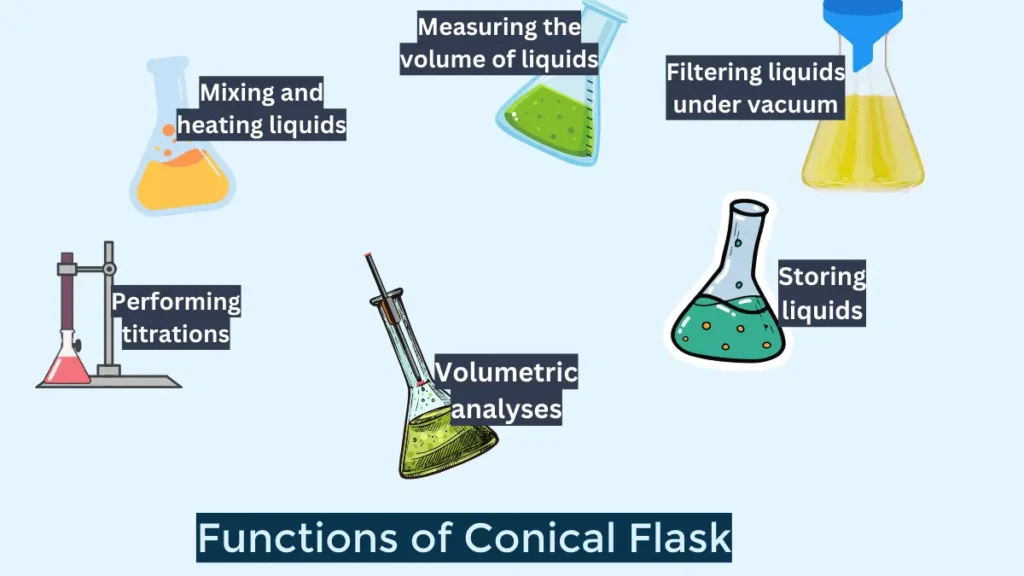
Uses Of Conical Flasks In Chemistry
Conical flasks are a common type of laboratory glassware that are used for a variety of purposes in Labortary. Here are a few function of conical flask:
1. Mixing and swirling liquids
The conical shape of the flask allows for easy mixing and swirling of liquids. This can be helpful for dissolving solids, mixing chemicals, and preparing samples for analysis.
2. Heating liquids
Conical flasks can be used to heat liquids for a variety of purposes, such as dissolving chemicals, conducting chemical reactions, and preparing samples for analysis. Conical flasks are typically made of heat-resistant materials such as glass or borosilicate glass.
3.Titrations
Conical flasks are commonly used for titrations, which are a type of quantitative analysis that involves the reaction of two solutions of known concentrations. The conical shape of the flask makes it easy to see the endpoint of the titration.
4. Volumetric analyses
Conical flasks can also be used for volumetric analyses, which are a type of quantitative analysis that involves the measurement of the volume of a liquid. Conical flasks with graduations can be used to measure the volume of liquid in the flask.
5. Storage
Conical flasks can also be used to store liquids. However, it is important to note that conical flasks are not airtight, so they should not be used to store volatile or corrosive liquids.
6. Recrystallization
Conical flasks can be used for recrystallization, which is a process of purifying a solid by dissolving it in a hot solvent and then cooling the solution slowly so that the solid recrystallizes.
7. Distillation
Conical flasks can be used for distillation, which is a process of separating two liquids with different boiling points.
8. Filtration
Conical flasks can be used for filtration, which is a process of separating a solid from a liquid by passing the mixture through a filter.
Uses Of Conical Flasks In Biology
Conical flasks are a versatile and essential piece of laboratory equipment that can be used for a variety of purposes in biology. The conical shape of the flask provides a large surface area for cell growth and gas exchange, making it ideal for preparing and storing cell cultures.
Conical flasks can also be used to perform titrations, measure the volume of liquids, mix and heat liquids, and filter liquids under vacuum.
Use of conical flask as a reaction vessel
Conical flasks are commonly used as reaction vessels because they offer a number of advantages over other types of laboratory glassware.
- Shape – The conical shape of the flask provides a large surface area for the reactants to come into contact with each other, which helps to speed up the reaction. The conical shape also helps to prevent the flask from tipping over.
- Narrow neck – The narrow neck of the flask helps to prevent the evaporation of volatile liquids and the escape of gases. This is important for reactions that produce gases, as it prevents the gases from escaping into the laboratory environment.
- Volume – Conical flasks come in a variety of sizes, making them suitable for a wide range of reactions. Conical flasks can be used for reactions that involve small volumes of reactants, as well as reactions that involve large volumes of reactants.
- Material – Conical flasks are typically made of glass or plastic, which are both inert materials that will not react with the reactants. This is important for reactions that involve highly reactive chemicals, as it prevents the chemicals from reacting with the glassware.
Use of conical flask as a condenser
A conical flask can be used as a condenser in a simple distillation setup. The flask is filled with cold water and placed in a vertical position, with the narrow neck pointing downwards. The neck of the flask is then connected to the distillation column using a rubber stopper.
As the vapors from the boiling liquid rise up the distillation column, they are cooled by the cold water in the conical flask. The cooled vapors then condense back into a liquid and drip into a collection flask placed below the condenser.
Conical flasks are typically made of glass, which is a good conductor of heat. This makes them effective at transferring heat from the vapors to the cold water in the flask. Conical flasks are also relatively inexpensive and easy to obtain, making them a practical choice for use as condensers in simple distillation setups.
Use of conical flask as burette
A conical flask can be used as a burette in a pinch, but it is not ideal for this purpose. Conical flasks do not have the same level of accuracy and precision as burettes, and they are more difficult to control.
To use a conical flask as a burette, you will need to make a few modifications. First, you will need to find a way to control the flow of liquid from the flask. This can be done by attaching a stopcock to the neck of the flask, or by using a piece of rubber tubing with a clamp.
Second, you will need to find a way to measure the volume of liquid dispensed from the flask. This can be done by marking the flask with graduations, or by using a separate measuring cylinder.
Once you have made these modifications, you can use the conical flask as a burette to perform titrations and other volumetric analyses. However, it is important to note that the results of your analyses may not be as accurate as if you were using a dedicated burette.
Filtering Flask
A heavy conical flask with an inlet for vacuum and an opening that fits a Buchner funnel is called a filtering flask. It is a type of laboratory glassware that is used to filter liquids under vacuum.
The filtering flask is typically made of thick glass or borosilicate glass, which makes it durable and able to withstand the pressure of the vacuum. It has a conical shape, which helps to prevent the flask from tipping over.
The inlet for vacuum is located at the bottom of the filtering flask. It is connected to a vacuum pump using a vacuum hose. The opening that fits a Buchner funnel is located at the top of the filtering flask. The Buchner funnel is placed in the opening and sealed with a rubber stopper.
To use a filtering flask, the liquid to be filtered is placed in the Buchner funnel. The vacuum pump is turned on, which creates a vacuum in the filtering flask. The vacuum causes the liquid to be drawn through the filter paper in the Buchner funnel and into the filtering flask.
Once the liquid has been filtered, the vacuum pump is turned off and the Buchner funnel is removed. The filtered liquid can then be collected from the filtering flask.