written by Adeel Abbas
If you have ever taken a chemistry class then you probably know about indicators – substances that are used to determine the pH of a solution.
Indicators are an essential tool in a variety of scientific and medical applications, but did you know that there are two main types of indicators? In this blog post, we will learn the differences between natural and synthetic indicators.
Natural Indicators
Natural indicators are substances that occur naturally and are used to determine the pH of a solution. Some examples of natural indicators include:
- Red cabbage
- Turmeric
- Blueberries
- Beets
The color of a natural indicator solution can change depending on the pH of the substance it is added to. For example, red cabbage indicator will turn pink in a basic solution and purple in an acidic solution.
Synthetic Indicators
Synthetic indicators, on the other hand, are man-made and are often used in scientific settings such as laboratories. Some examples of synthetic indicators include:
- Phenolphthalein
- Bromothymol blue
- Methyl orange
Synthetic indicators can be used to measure pH over a wider range than natural indicators. They are also more stable and longer-lasting, making them a more practical choice for certain applications.
Differences Between Natural and Synthetic Indicators
The main differences between natural and synthetic indicators:
- Origin: Natural indicators are derived from plants, while synthetic indicators are man-made.
- Precision: Synthetic indicators are generally more precise and reliable than natural indicators.
- Range: Synthetic indicators can be used to measure pH over a wider range than natural indicators.
- Stability: Synthetic indicators are more stable and longer-lasting than natural indicators.
- Uses: Natural indicators are often used in traditional or alternative medicine and food preparation, while synthetic indicators are more commonly used in scientific settings such as laboratories.
- Availability: Natural indicators may be more difficult to obtain and may vary in quality, while synthetic indicators are more readily available and consistent.
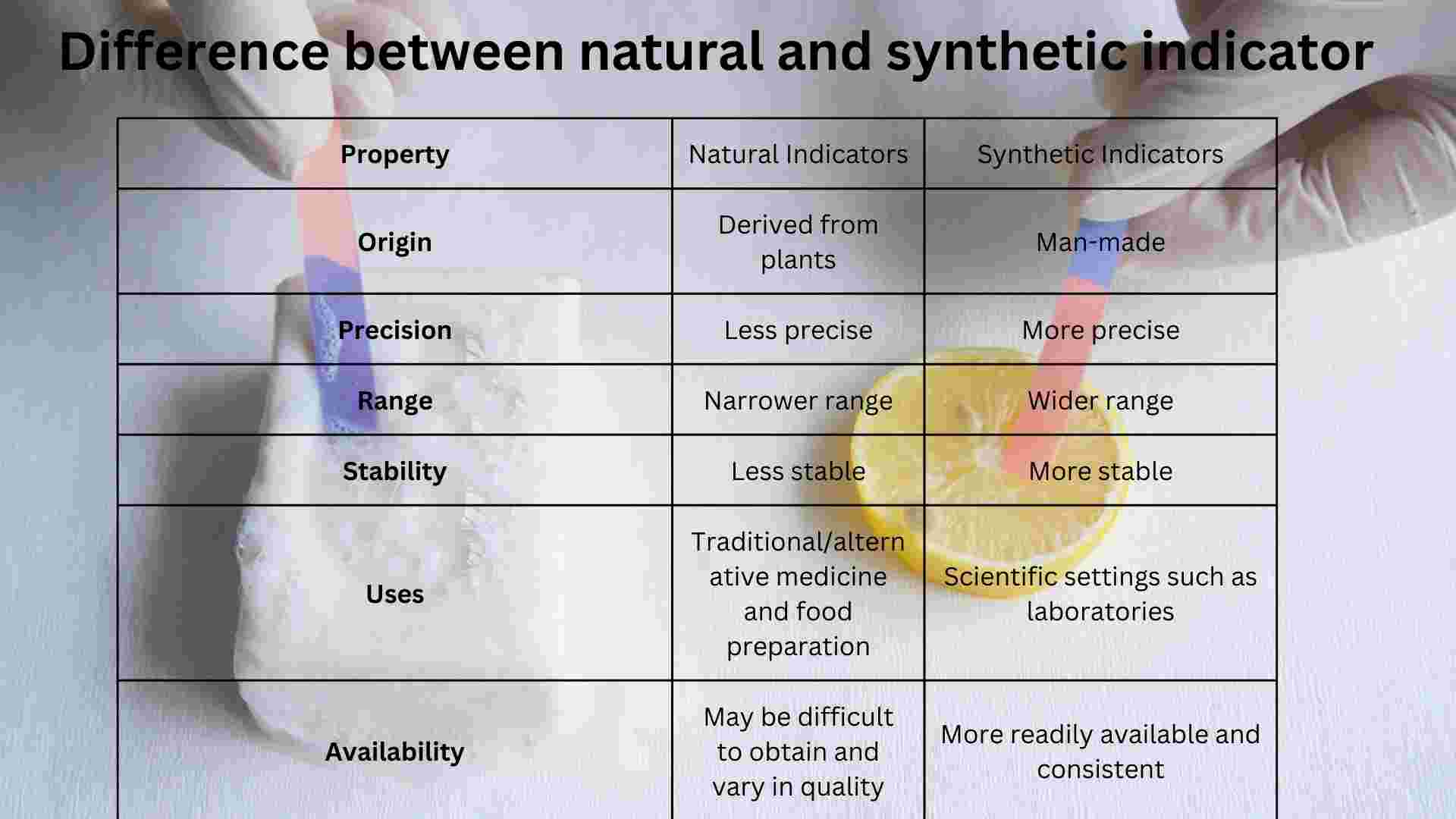
Here is the comparison between natural and synthetic indicators in table format:
| Property | Natural Indicators | Synthetic Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Derived from plants | Man-made |
| Precision | Less precise | More precise |
| Range | Narrower range | Wider range |
| Stability | Less stable | More stable |
| Uses | Traditional/alternative medicine and food preparation | Scientific settings such as laboratories |
| Availability | May be difficult to obtain and vary in quality | More readily available and consistent |