Written By Adeel Abbas
Distillation can be used to separate mixtures of liquids with different boiling points, such as ethanol and water, acetone and water, and benzene and toluene. All of these mixtures can be separated by distillation because the components of the mixture have different boiling points.
Distillation is a common method of separating mixtures. It involves heating a mixture to vaporize one or more of its components and then cooling and condensing the vapor.
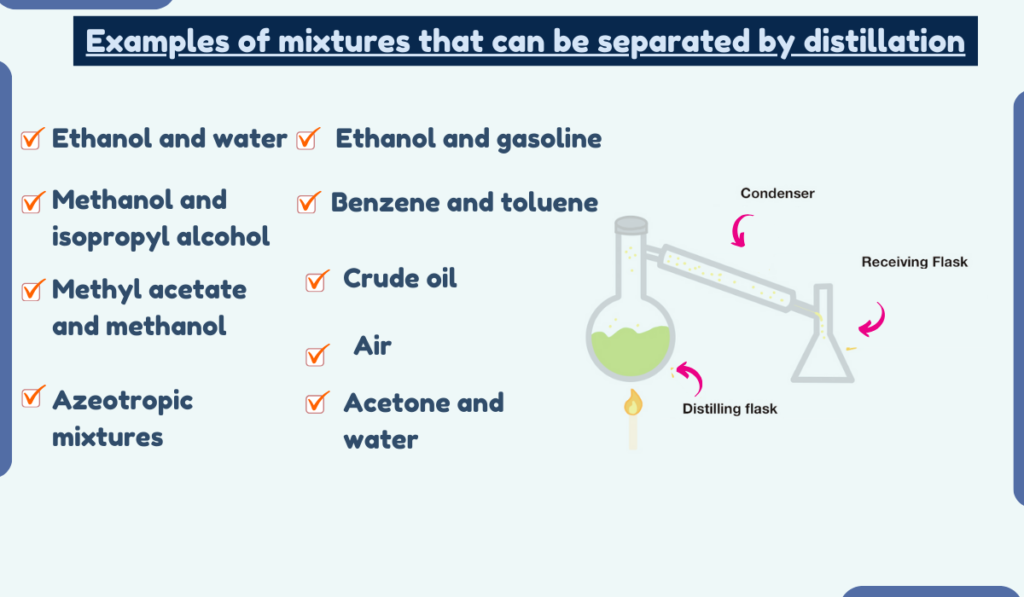
Examples of mixtures that can be separated by distillation
Table of Contents
Here are 19 examples of mixtures that can be separated by distillation.
1. Ethanol and water
Ethanol and water have different boiling points, so they can be separated by distillation. Ethanol boils at a lower temperature than water, so it will evaporate first. The ethanol vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid, which will be a higher concentration of ethanol.
2. Crude oil
Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons and other compounds with different boiling points. Distillation is used to separate the various components of crude oil based on their boiling points. This process is called oil refining.
3. Azeotropic mixtures like HCl and water
Azeotropic mixtures are those in which the boiling point of the mixture is the same as that of one of its components. For example, a mixture of 20.2% hydrochloric acid (HCl) and 79.8% water has the same boiling point as pure HCl. Distillation can be used to break these mixtures into their individual components by adding another component to the mixture that changes the boiling point. For example, adding salt to the HCl-water mixture will change the boiling point of the mixture so that the HCl can be distilled off.
4. Air
Air is a mixture of gases with different boiling points. Distillation can be used to separate the different components of air, such as nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. The process is based on the different boiling points of the gases.
5. Acetone and water
Acetone has a lower boiling point than water, so it can be separated from water by distillation. The acetone vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid, which will be a higher purity of acetone.
6. Ethanol and gasoline
Ethanol has a higher boiling point than gasoline, so it can be separated from gasoline by distillation. The ethanol vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid, which can be reused or disposed of.
7. Methyl acetate and methanol
Methyl acetate has a higher boiling point than methanol, so it can be separated from methanol by distillation. The methyl acetate vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
8. Benzene and toluene
Benzene has a lower boiling point than toluene, so it can be separated from toluene by distillation. The benzene vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
9. Cyclohexane and toluene
Cyclohexane has a lower boiling point than toluene, so it can be separated from toluene by distillation. The cyclohexane vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
10. Water and methanol
Methanol has a lower boiling point than water, so it can be separated from water by distillation. The methanol vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
11. Methanol and acetone
Acetone has a lower boiling point than methanol, so it can be separated from methanol by distillation. The acetone vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
12. Methanol and isopropyl alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol has a higher boiling point than methanol, so it can be separated from methanol by distillation. The isopropyl alcohol vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
13. Methyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol
Ethanol has a higher boiling point than methanol, so it can be separated from methanol by distillation. The ethanol vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
Nitric acid and water: Nitric acid has a lower boiling point than water, so it can be separated from water by distillation. The nitric acid vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
14. Hexane and heptane
Hexane has a lower boiling point than heptane, so it can be separated from heptane by distillation. The hexane vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
15. Ethyl acetate and ethanol
Ethyl acetate has a lower boiling point than ethanol, so it can be separated from ethanol by distillation. The ethyl acetate vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
16. Butanol and water
Butanol has a higher boiling point than water, so it can be separated from water by distillation. The butanol vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
17. Aniline and water
Aniline has a higher boiling point than water, so it can be separated from water by distillation. The aniline vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
18. Ethylene glycol and water
Ethylene glycol has a higher boiling point than water, so it can be separated from water by distillation. The ethylene glycol vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.
19. Glycerol and water
Glycerol has a higher boiling point than water, so it can be separated from water by distillation. The glycerol vapor can then be condensed back into a liquid.