LEARNING OBJECTIVES
In this article, author has explained the introduction, structure, properties, functions, uses and cellulolysis reaction of cellulose.
Cellulose is a complex polysaccharide made up of many glucose monosaccharides. It consists of about 3000 or more glucose units. Cellulose is the most abundant carbohydrate in plants. It is major component of plants cell wall. Cellulose is most abundant organic compound.
Humans cannot digest cellulose due to lack of enzyme “cellulase”.
Structure of cellulose
Table of Contents
Cellulose consists of β-D-glucose units. The β-D-glucose units are linked by β 1, 4 glycosidic linkages
.
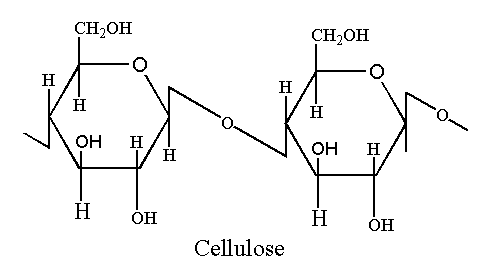
The glycosidic bond is in beta orientation. The cellulose has linear structure. It does not have branching like glycogen and starch.
Properties of cellulose
- Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound exists on the earth.
- It is complex polysaccharide that consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
- The molecular formula of cellulose is (C6H10O5)n.
- The molecular mass of cellulose is 162.1406g/mol.
- The density of cellulose of 1.5g/cm3.
- The melting point of cellulose is 260-2700C.
- Cellulose possesses high tensile strength due to presence of alternate hydrogen bonds.
- It is an odorless compound.
- Cellulose is insoluble in water.
- It is a tasteless compound.
- It is a biodegradable compound.
- Natural cotton consists of 90%cellulose.
- Wood contains about 45% cellulose.
- It is soluble in organic solvents.
- Cellulose is a crystalline compound.
- It also exists in powder form.
Functions of cellulose
- The main function of cellulose is to provide support to the plants. It is a major component of plant’s cell wall. It gives strength and rigid structure to the plants. In plants, cellulose is present in lignin matrix. The lignin also provides strength to plants.
- Plant cells stand against turgor pressure with the help of cellulose.
- Cellulose is also major component of cell wall of many microorganisms like bacteria and algae. It provides rigidity. In addition, it also maintains structure and shape of these microorganisms.
- In some bacteria, cellulose functions to produce biofilms. Biofilms in the microorganisms provide the point of attachment and allow them to organize in colonies.
- Many bacteria break cellulose to produce glucose. This glucose is use as a source of carbon to produce energy.
- Animals cannot make their own cellulose. But it is essential for them. Animals get cellulose in the form of plants they eat. Herbivores have microorganisms in the intestine which contains the enzyme cellulase. Thus herbivores can digest cellulose.
- Cellulose is a food for the insects. In insects, cellulose also acts as basic building material.
- Humans cannot digest cellulose due to absence of enzyme “cellulase”. Therefore, humans consume cellulose in the form of fibers through the diet.
Uses of cellulose
- During the separation of proteins by paper chromatography, cellulose is use as stationery phase.
- Cellulose is used in the production of explosives.
- It is use in to make nitrate filter membranes.
- It is use as emulsifier.
- Cellulose is use to make rayon.
- Use as a jelling agent.
- Use to produce nitrocellulose.
- Cellulose is widely use in the production of paper and paperboards.
- Humans use cellulose as fiber in diet.
- Use in various food items as an additive.
- Cellulose is use in many textile industries.
- It is use to make different kind of fibers like cotton, linen etc.
- The powder form of cellulose is use as drug filler.
- It is use a building material.
- Use as an electrical insulator.
- Cellulose is processed to use it as a biofuel.
- Besides these uses, we use cellulose in household items on daily basis like in laxatives, sponges, eye drops, glues, coffee filters etc.
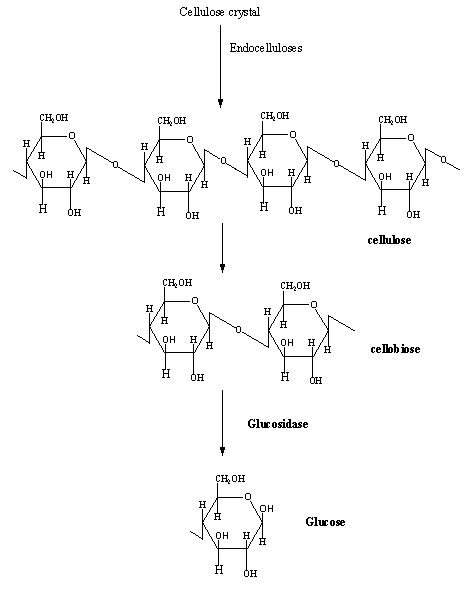
Cellulolysis
The hydrolysis of cellulose is called cellulolysis. Hydrolysis is reaction of cellulose with water. Two types of enzymes are involved in the cellulolysis; endocellulases and exocellulases.
Endocellulases breakdown the non-covalent interactions present in the cellulose. It breaks the crystal structure of cellulose to amorphous structure.
Exocellulases are the enzymes that break long polymer chain into small fragments of sugars like cellobiose and cellotetraose.
Cellobiose is the combination of two glucose units while cellotetraose is the combination of four glucose units.
The last step is the hydrolyzation of cellubiose or cellotetraose to form glucose. This step is catalyzed by β-glucosidases.