LEARNING OBJECTIVES
In this article, author has explained the introduction, structure, functions and storage diseases of glycogen.
Glycogen is a polysaccharide made up of many units of glucose monosaccharide. It is use to store energy in the animals hence also refer as “animal starch”. Glycogen is present in liver, muscles and brain. When glucose is more than we need, the excess glucose is store in the form of glycogen in the body. When glucose is deficient, glycogen breaks into glucose.
Structure of glycogen
Table of Contents
The structure of glycogen is similar to amylopectin but glycogen has more branches as compare to amylopectin.
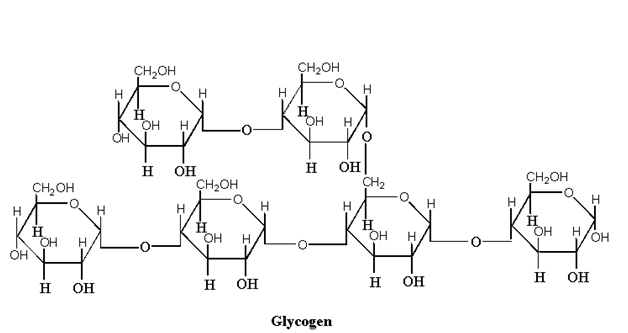
The glucose units are linked by α 1, 4 glycosidic bond. At branch point 1, 6 glycosidic linkages are present.
Functions of glycogen
Glycogen is mainly found in liver and muscle cell. It functions to provide glucose, when glucose level is low in cell.
1. Liver cells
When we take diet, blood glucose increases. When blood glucose level increase, insulin in pancreas gets activated and promotes the uptake of glucose in liver cells. The enzyme necessary for the synthesis of glycogen “glycogen synthase” also activates by insulin. When glucose level is high, the monomers of glucose link to form glycogen. The glycogen is formed through the process of “glyconeogenesis”. In this way, excess glucose is stored in the form of glycogen.
When glucose and insulin level drops, the glycogen synthesis stops. When glucose level falls, the enzyme needed for the breakdown of glycogen “glucagon” is released from the pancreas. The glycogen breaks through the process of “glycogenolysis”.
In this way when glucose level is high the excess glucose is stored in the form of glycogen and when blood glucose level is low the glycogen breaks down to provide glucose.
2. Muscle cells
Glycogen is also stored in muscles. The glycogen stored in muscles is greater than the glycogen stored in the liver. During exercise glucose level is low than normal. In this condition, glucose-1-phosphate produces by the breaks down of glycogen is converted to glucose-6-phosphate which provides energy during the stress condition.
3. Other tissues
Glycogen is also found in other tissues where it provides energy. It is found in uterus where it provides energy to embryo. Besides this, glycogen is found in kidney cells, red blood cells and white blood cells. It is also found in glial cells.
4. Microorganisms
In microorganisms like fungi and bacteria, glycogen is the main energy storage carbohydrate. When resources are limited, these microorganisms use glycogen as a source of energy. When surplus carbon is available, bacteria form the glycogen for later use. When nutrients like sulfur, carbon and phosphorus are not available bacteria and fungi use stored glycogen.
Glycogen storage diseases
The metabolic defects concerned with the synthesis and breakdown of glycogen are called glycogen storage diseases. These defects are related to abnormal deposition of glycogen in one or more tissues like muscles, liver and brain. The disorders are due to some defects in glycogen synthesis and degradation enzymes.
1. Von Gierke’s disease
Von Gierke disease is also known as glycogen storage type 1 disease. This disease is due to defects in enzyme glucose-6-phosphate. When this enzyme is not working normal, glycogen is not break into glucose. Glycogen level increase in the tissues and glucose is not released. When glycogen does not break, blood glucose level gets low.
This disease is inherited and runs through the families.
2. Pompe disease
It is also known as glycogen storage type II disease. This disease is due to defects in lysosomal α-1, 4 glucosidase enzyme. Glycogen does not break to glucose and accumulates in the many organs like heart, brain etc. this disease can cause the damage to heart and brain. Liver may also get enlarged. Person may get die due to heart attack or abnormal functioning of nervous system.
This disease is also inherited.
3. Cori’s disease
This disease also known’s as storage type III disease is due to defect in enzyme amylo α-1, 6 glucosidase. The branched chain glycogen gets accumulated in liver muscles and leucocytes. This can cause dysfunction of these organs.
4. Anderson’s disease
Anderson’s disease is called storage type IV disease. This is due to disruption in glucosyl 4, 6 transferase enzyme. The abnormal amount of glycogen accumulates in the liver. Liver gets enlarged. Liver does not function normally due to this defect.
5. McArdle’s disease
It is also known as storage type V disease. This disease happens due to disruption in enzyme muscle glycogen phosphorylase. In this disease, the amount of glycogen in muscles is high. Therefore, during exercise enough energy is not available. Person may suffer from muscle cramps and muscles get damaged.
6. Her’s disease
It is also known as glycogen storage type VI disease. It is due to defect in liver glycogen phosphorylase enzyme. Glycogen stores in the liver. Liver gets enlarged. It can also cause hypoglycemia and ketosis.
7. Tauri’s disease
It is also known as glycogen storage type VII disease. It happens due to defect in phosphofructokinase enzyme. In this disease, person is unable to do exercise. Abnormal amount of glycogen stores in skeletal muscles and erythrocytes. Blood lactate does not increase. It can also cause hemolysis.