LEARNING OBJECTIVES
In this article, author has explained the introduction, structure, characteristics, classification, reactions, functions and uses of starch.
Definition of Starch
Table of Contents
Starch is a polysaccharide made up of thousands of units of monosaccharide glucose linked by 1, 4 glycosidic linkage.
It is a complex carbohydrate which stores energy in plants. It is found in leaves, roots, stem and fruits of plants. It is also known as “glucan”. The basic chemical formula of starch is (C6H10O5)n where n can be hundred to many thousands.
Structure of starch
Starch is a homopolysaccharide made up of repeating units of D-glucose linked by α-glycosidic bonds.
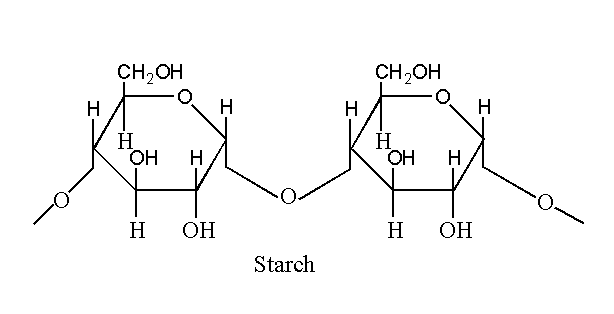
Glucose units are covalently bonded with the release of water molecule. OH group is release from one monosaccharide and hydrogen atom is release from another monosaccharide. The linkage is 1, 4 glycosidic linkage.
Characteristics of starch
- The molecular formula of starch is C12H22O11.
- It is a non-reducing sugar.
- Starch is tasteless carbohydrate.
- It is odorless compound.
- Pure starch is mostly extracted from the plants.
- It is use as food ingredient worldwide.
- The molecular mass of linear starch (amylose) is 105gmol-1.
- The molecular mass of branched starch (amylopectin) is 107gmol-1.
- Density of starch is 18gcm-3.
- Melting point is 256-2580C.
Classification of starch
Starch is classified into two classes on the basis of structure.
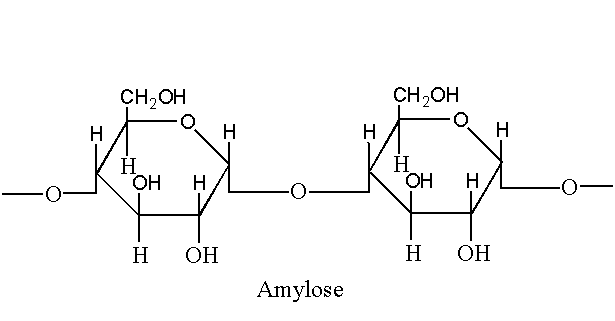
1. Amylose
The linear structure of starch is known as amylose. Amylose is an unbranched structure of D-glucose. It is soluble in water. Amylose contributes the less portion of starch about 20% only. Amylose is a long chain polymer consists of about 200-1000 glucose units. The glucose units are linked by 1, 4 glycosidic linkage.
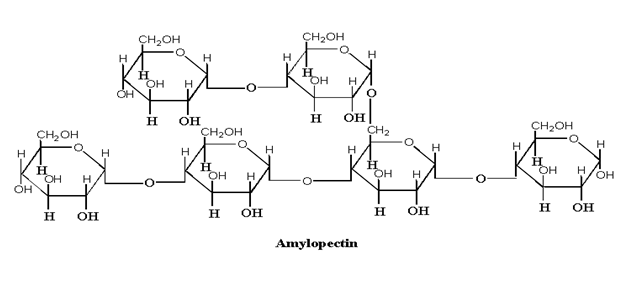
2. Amylopectin
The branched chain of starch is known as amylopectin. It is a branched structure of D-glucose units. Amylopectin is insoluble in water. It constitutes greater portion of starch about 80%. Amylopectin has some straight chain glucose while some are branched. The straight chain glucose is linked by 1, 4 glycosidic bond while 1, 6 linkage is present at branching point.
Reactions of starch
1. Hydrolysis
The addition of water that cleaves the bond and results in the cleavage products is called hydrolysis. When water is added to the starch, it produces glucose.
nC6H10O5 (starch) + nH2O —> nC6H12O6 (glucose)
2. Esterification
The reaction between alcohol and carboxylic acid to produce ester is called esterification reaction. This reaction usually happens under the acidic condition. In the case of starch, this reaction usually happens between the carboxylic group of fatty acids and alcohol group of glucose.
RCOOH + R’OH —> RCOOR’ + H2O
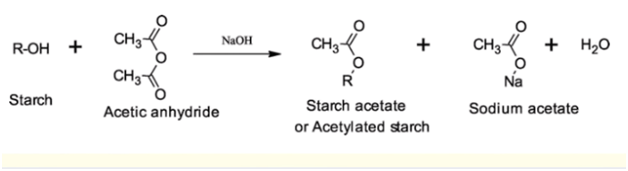
3. Acetylation of starch
When starch reacts with acetic anhydride to produce acetylated starch, this reaction is known as acetylation. The hydroxyl group of glucose is esterified with the acetyl group of acetic anhydride.
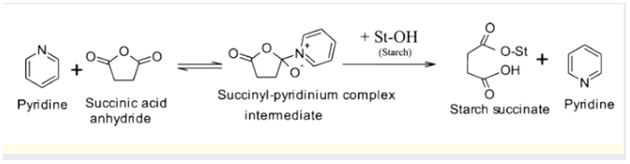
4. Succinylation of starch
When starch reacts with the succinyl anhydride, succinyl starch is produce. This reaction is known as succinylation of starch.
5. Phosphorylation of starch
Starch reacts with pyrophosphoric acid to produce phosphoric acid and starch phosphate.
St-OH (starch) + H4P2O7 (pyrophoshoric acid)—> St-O-H2PO3 (starch phosphate)
Functions of starch
- The main function of starch is to store energy/glucose in the plants. The leaves of plant absorb sunlight and make glucose through the process of photosynthesis. Plants take water, sunlight and carbon dioxide to carry the process of photosynthesis. The excess glucose is store in the form of starch. So, the main function of starch is to store energy in the plants. The stored starch is use at night by the plants. The starch is store in the specific organelle of plants called amyloplast.
- Our body only uses glucose as a source of energy. When we take in green fruits and vegetables, starch enters in our body and breaks into glucose. The enzyme amylase present in our body catalyzes the starch. This glucose is use by brain and muscles as a source of energy. So, starch acts a fuel for our body.
- Besides these, starch has also another important function. Starch food contains many essential minerals like iron, calcium and folate. These minerals are important for our body.
Uses of starch
- Starch is use to store energy in plants.
- It is use to provide energy/glucose in human body especially to brain and muscles.
- Use in many foods like noodles, soups, custard, gravies, puddings and pasta etc.
- Use in wet granulation process.
- Use in animal feed.
- Use in dairy products.
- Use in beverages.
- Use in agrochemical industry.
- Use in detergents as bleaching agent.
- Use in the formulation of tablets and pills.
- Use in pharmaceutical industries.
- Use in adhesives.