Learning objectives
In this article the author has explained stoichiometry and limiting reactant.
What is Stoichiometry?
Table of Contents
The branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the relationship between the quantities of reactions and products as given by a balanced chemical equation is called stoichiometry.
Definition of stoichiometry
Advantages and Limitations of a chemical equation
Consider the following reaction

This equation tells that 1 mole of Carbon reacts with 1 mole of Oxygen to give one mole CO2. Therefore, this equation can be used to study the quantitative relationship between reactants and products.
Limitations of a chemical equation
When we talk about the chemical equations, these do not tell us about the following factors.
- Conditions such as temperature and pressure
- Rate of reaction
- The physical state of reactants and products
- Mechanism of reaction
The following types of relationship can be studied with the help of a balanced chemical equation.

Stoichiometry calculations are based on the following assumptions:
- All reactants are converted into products.
- Only the desired reaction occurs.
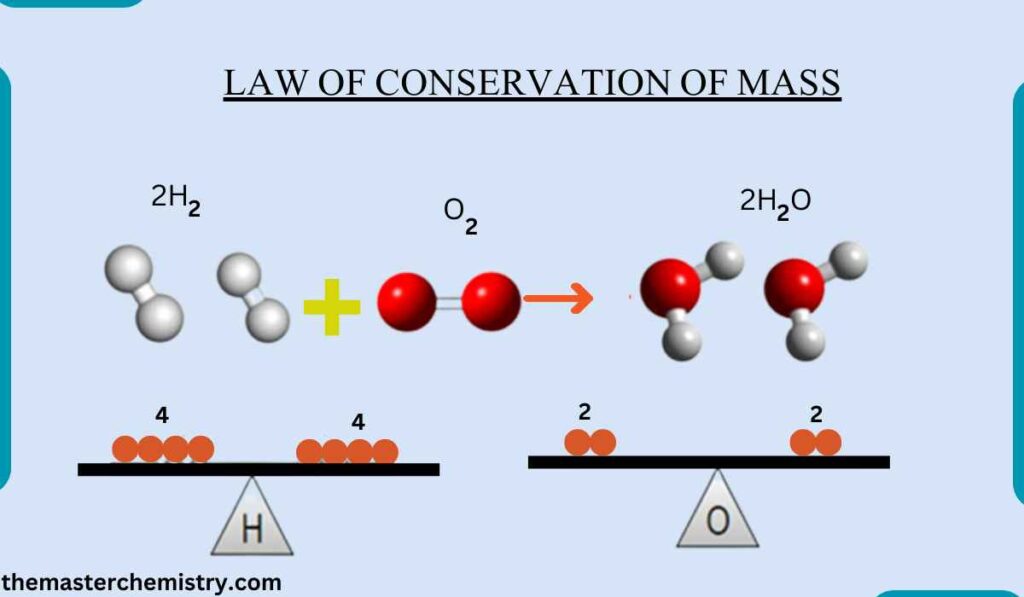
- Law of conservation of mass: The total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products.
- A given chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass.
According to the law of conservation of mass,
Mass can neither be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Definition of law of conservation of mass
It can also be defined as total mass of reactants is equal to the total mass of products.
Therefore, total number of atoms entering into a chemical reaction is equal to the total number of atoms in the products.
According to the law of definite proportions
A pure chemical compound always contains the same elements combined in the same ratio by weight.
Law of definite proportion

Stochiometric relationships
Mass-Mass relationship
With the help of mass of given substance, mass of another substance can be calculated.
Mass-Mole relationship
With the help of mass of one substance volume of the other substance can be calculated and vice versa.
Mole-Mole relationship
With the help of moles of a given substance, mole of another substance can be calculated.
Also read: Avogadro’s number and molar volume
Limiting reactant
A limiting reactant is a reactant that controls the amount of the products formed in a chemical reaction due to being less than the required amount.
Definition of limiting reactant
It can also be defined as follow:
It is a reactant that produces the least number of moles of product.
It is consumed earlier in the reaction.
Identification of limiting reactant
- To identify a limiting reactant, the following three steps are performed.
- Calculated the number of moles from the given amount of reactants.
- Calculated the number of moles of product formed from the given moles of each reactant.
- Identify the reactant as limiting reactant which produces the least moles of product.
Example

When 2 moles of hydrogen (4g) react with 2 moles of oxygen (64g), then only 2 moles (36g) of water are produced. It is because 2 moles (4g) of hydrogen react with 1 mole 32g) of oxygen. Since less hydrogen is present than oxygen, so hydrogen is the limiting reactant.
Example 2
The burning of coal occurs in excess of oxygen. In this coal is the limiting reactant while oxygen is in excess.
Example 3
Rusting of iron occurs in excess of oxygen present in the air. In this, iron is the limiting reactant while oxygen is in excess.
Applications of deliberate use of limiting reactant
1. Complete consumption of expensive reactant
The other reactant are taken in large amount than the expensive reactants. It ensures that all of the expensive reactant is completely used up in the chemical reaction, so it becomes the limiting reactant.
2. To speed up the reaction
Rate of reaction is directly proportional to the amounts of reactants. Therefore a large quantity of one reactant may speed up the reaction. For example, a large quantity of oxygen burns things fatter. Thus excess of oxygen is left behind at the end of reaction and burning things like paper, wood are the limiting reactants.
Read More about:
Differences between Actual Yield and Theoretical Yield
Let others know about this