Learning Objectives
In this article, the author has explained the fractional distillation of petroleum products. After reading this article you will learn about the following points.
- Fractional distillation and crude oil
- Working of Fractionating column
- Different types of fractions of petroleum
What is fractional distillation?
Table of Contents
Fractional distillation is a process of separating the compounds of the mixture on the basis of differences in their boiling points.
Definition of fractional distillation
Crude oil
The mixture of different hydrocarbons which goes through the process of evaporation and condensation at carried temperatures in the fractionating column to give hydrocarbons with a similar range of boiling points is known as crude oil.
Definition of crude oil
Why there is a need for fractional distillation?
When the explorers discover the oil reserves, the crude oil obtained from them is not in pure form. There are many types of fuels in this crude oil.
To separate the different fractions of petroleum from this impure petroleum reserve, fractional distillation is performed.
Schematic diagram of fractional distillation of petroleum
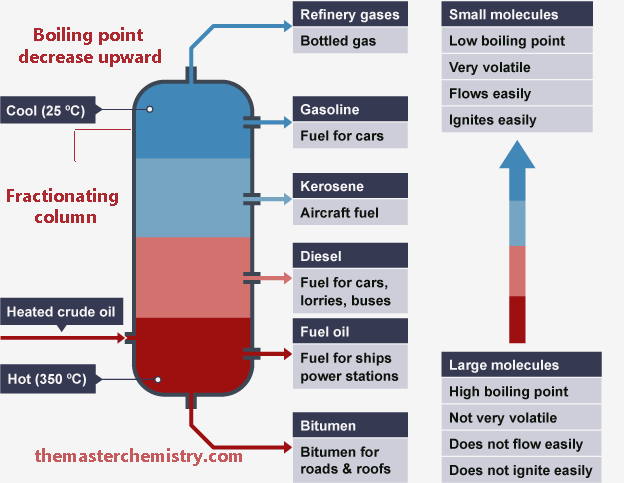
As we move from top to bottom the hydrocarbons with higher molecular mass and boiling points are separated. Their appearance is also sticky and waxy.
When we move from bottom to top in fractionating column hydrocarbons with lower molecular mass and boiling points are separated. These are basically burning fossil fuels and can be ignited with a little spark.
Also read: The sources of organic compounds
which products are obtained from the fractional distillation of petroleum?
The names of different fractions along with their uses are given below.
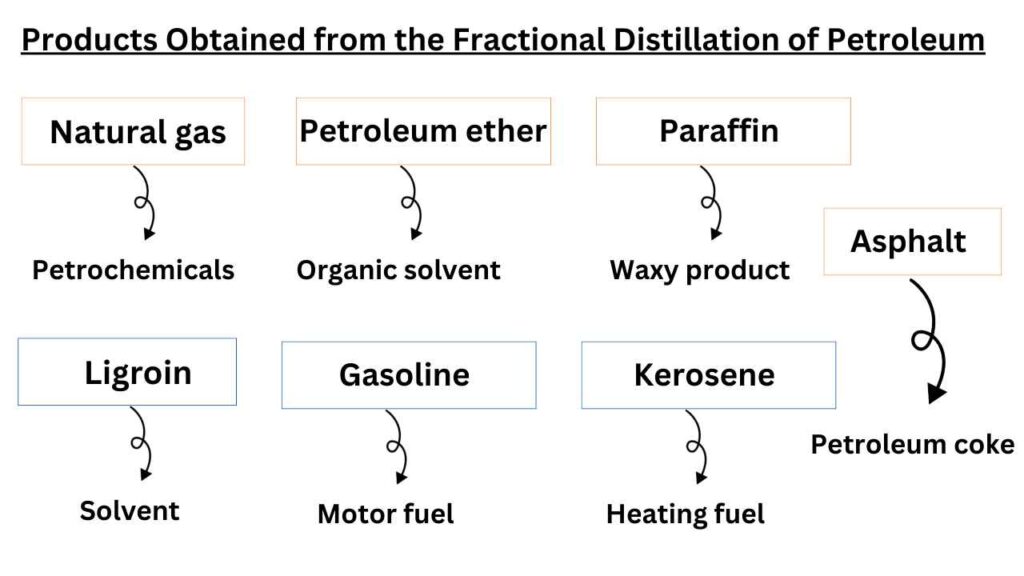
Natural gas
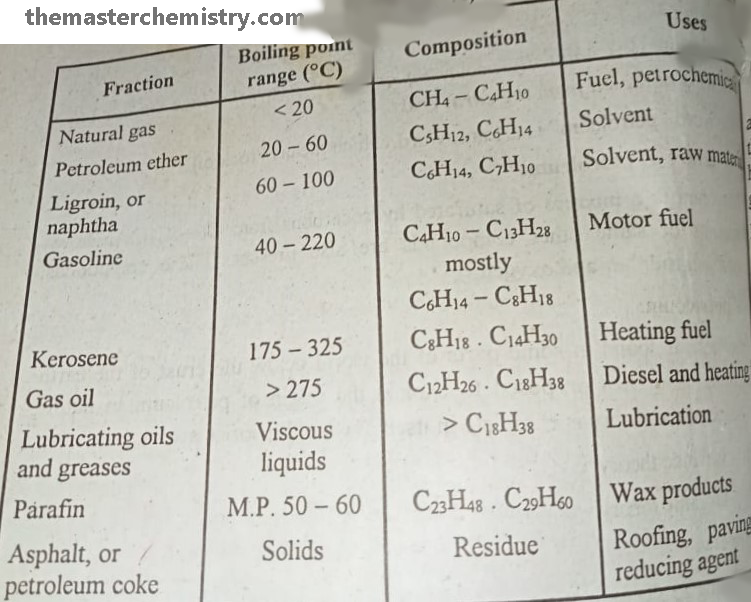
It is methane gas that we use in household activities. Their boiling points range is < 20 °C . The composition of natural gas is CH4-C4H10. It is used as fuel and petrochemicals.
Petroleum ether
It is a organic solvent that is obtained in the range of 20 -60 °C boiling point. Mostly it contains the hydrocarbons with C5H12, C6H14. It is used as the organic solvent in synthetic and natural product chemistry.
Ligroin or maphtha
It is a solvent with boiling points range of 60-100 °C. The hydrocarbon members of this range are C6H14, C7H10. It is used as solvent and raw material in many industrial actions.
Gasoline
It is also known as motor fuel. The boiling point range of hydrocarbons in this family is 40-222 °C. It is composed of hydrocarbons C4H10-C13H28.
Kerosene
It is used as heating fuel and boiling point range of hydrocarbons present in it is 175-325 °C. The hydrocarbons in this range are composed of C8H18, C14H30.
Gas oil
It is also used as heating and diesel fuel. Its boiling points range from >275 °C and composed of C12H26, C18H38.
Lubricating oils and greases
As name indicates that the hydrocarbons of this fraction are used as lubrication purpose. Apparently, these are viscous liquids and are composed of > C18H38.
Paraffin
These are waxy products and composed of C23H48, C29H60.
Asphalt or petroleum coke
These are solids by appearance. The hydrocarbons in these fractions are composed of Residue. It is used for roofing, paving, fuel, and reducing agents.
Summarized form of different fractions obtained after Fractional distillation of Petroleum
Let other know about this