LEARNING OBJECTIVES
In this article, the author has explained 6 differences between CNG and LPG in detail.
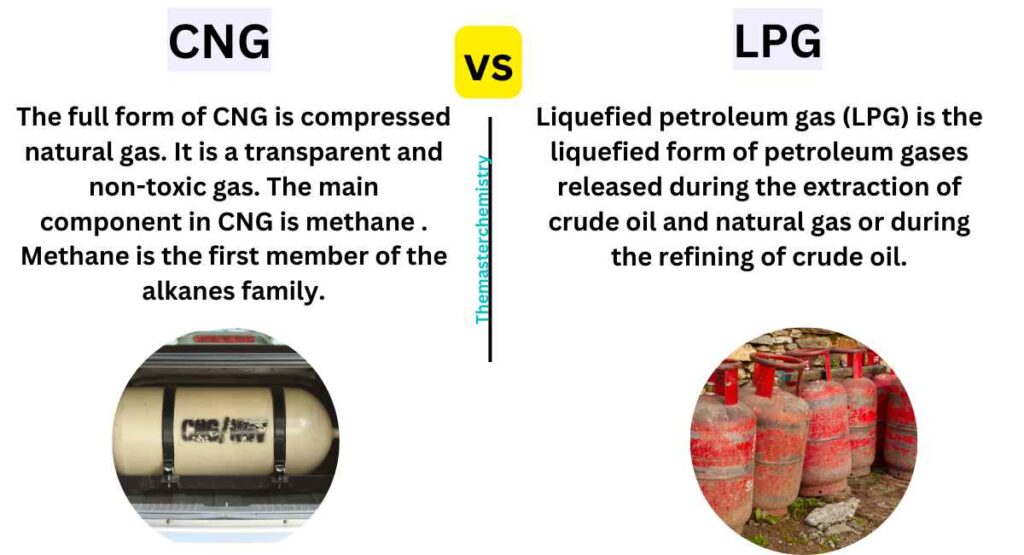
The main difference between CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) and LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) is the difference of their composition. CNG primarily consists of methane, while LPG primarily consists of propane. CNG is considered safer than LPG due to its better dispersal properties. CNG is stored in a vehicle’s tank in gaseous form, while LPG is stored as a liquid obtained by compressing and cooling natural gas to extremely low temperatures.
CNG vs LPG Table
Here is a table summarizing the differences between CNG and LPG:
| Difference | CNG | LPG |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure requirement for usage | Requires higher pressure for use as a motor vehicle fuel | Does not require high-pressure transportation |
| Energy density | Lower energy density compared to LPG | Higher energy density |
| Flammability | Methane can burn with only 5% oxygen, while LPG requires 23% oxygen | LPG is less flammable than methane |
| Octane rating | Higher octane rating, resulting in more powerful engines | Lower octane rating |
| Source | Fossil fuel | Not a fossil fuel |
| Safety considerations | Higher vapor pressure and larger pressure differences between cold and hot fill-up | Lower vapor pressure and smaller pressure differences |
6 Difference Between CNG and LPG
1: The main difference Between CNG and LPG is that CNG requires higher pressure to be used as a motor vehicle fuel and LPG does not require the same kind of high-pressure transportation.
LPG does not require the same kind of high-pressure transportation or storage because it can exist naturally at or near atmospheric pressure, but it is still a dangerous substance that requires proper storage and transportation.
2: The second Difference Between CNG and LPG is the higher energy density of natural gas.
In fact, if we convert standard cubic feet to liters or kgs then methane has an equivalence ratio of approximately 12:11 (LNG), 27:15 (CNG), and 33:22 kg.
LPG has an equivalence ratio of approximately 36 to 44, which makes it difficult for consumers to store enough gas in their tanks to drive any reasonable distance or time before needing more fuel.
3: The third Difference Between CNG and LPG is the flammability of each substance. Methane can burn with just five percent oxygen while propane needs 23 per cent oxygen – that’s why propane vapors are often used by firefighters as a way of burning off excess material when fighting fires in close quarters.
4: The fourth Difference Between CNG and LPG is that CNG has a higher octane rating than LPG which makes for more powerful engines.
5: The fifth Difference Between CNG and LPG is that CNG is a fossil fuel and LPG is not. The Difference Between CNG and LPG is in this way, which means that Gasoline can be burned with either one of them; however, Diesel cannot work when you use the CNG substance because it will explode! This Difference Between CNG and LPG also says that one should take note to make sure they do not put diesel into their car if they choose to use the U-tube device for natural gas conversion kits.
6: The sixth Difference Between CNG and LPG is based on safety. Natural gasoline (CNG) has higher vapor pressure than conventional gasoline (~55 psi at 100 °F vs ~40 PSIG at 100° F), so NGVs tend to have larger (typically 12% to 20%) differences between cold and hot fill-up pressure.
Related articles