Learning Objectives
In this article, the author has explained about electrical conductivities of elements in the periodic table and conductivity trend periodic table. After reading this article you will learn the following topics.
- Electrical conductivity periodic table
- Conductivity trend periodic table
- Electricity periodic table
What is electrical conductivity in chemistry?
Table of Contents
Electrical conductivity is the capability of a substance to conduct the electric current due to the presence of free electrons without changing the composition of the substance.
Definition of electrical conductivity
In chemistry, electrical conductivity is a measure of a substance’s ability to conduct electricity. It is usually expressed in terms of a substance’s conductivity coefficient, which is the reciprocal of its electrical resistivity. The conductivity coefficient is a measure of the ease with which a substance allows the flow of electric charge through it.
The electrical conductivity of a substance can be affected by various factors, such as its temperature, pressure, and chemical composition.
Electrical conductivity is an important property of many materials and is often used to classify and characterize them.
Materials that are good conductors of electricity, such as metals, are used in the construction of electrical wires and other components in electrical circuits, while materials that are poor conductors, such as insulators, are used to protect people from electrical shocks and to prevent the unwanted flow of electricity in circuits.
What class of elements conduct electricity
Elements that belong to the following classes generally conduct electricity:
- Metals: Most metals, such as copper, aluminum, silver, and gold, are good conductors of electricity.
- Semimetals: Some semimetals, also known as metalloids, such as silicon and germanium, can also conduct electricity, but not as well as metals.
- Electrolytes: Some elements, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, are electrolytes and can conduct electricity when they are dissolved in water or other solvents.
Electrical conductivities of metals
Normally when we talk about the electrical conductivity, metals comes first in mind. Metals are considered the good conductors of electricity because of presence of free electrons.
However, there are certain elements other than metals with the ability of electrical conductance. Below given is the details of elements that can conduct electricity.
Also read
How to find electrical conductivity of elements?
What groups on the periodic table are good conductors of electricity?
The elements that are generally good conductors of electricity belong to the following groups on the periodic table:
- Group 1: The alkali metals, such as lithium, sodium, and potassium, are highly conductive.
- Group 2: The alkaline earth metals, such as beryllium, magnesium, and calcium, are also good conductors.
- Groups 3-12: The transition metals, which include elements such as copper, silver, and gold, are generally good conductors of electricity.
- Group 13: The elements in group 13, which include aluminum, gallium, and indium, are also good conductors.
- Group 14: The elements in group 14, which include silicon and germanium, are semimetals and are not as good conductors as the metals, but they can still conduct electricity to some extent.
Reason for electrical conductivity in periodic table
There is a close link between free electrons and electrical conductivity. The property of electrical conductivity is mainly due to the presence of a relatively large number of electrons in the outermost shell of the elements. Moreover, these electrons should feel easy for the movement in their lattice.
Conductivity trend periodic table
- The elements of group I-A and II-A decrease their electrical conductivities from top to the bottom in a group.
- The elements of group I-B i.e., Cu, Ag, Au are called coinage metals These have higher values of electrical conductance,
- The elements of group VI-A and VII-A i.e., oxygen and halogen family members show very low electrical conductance.
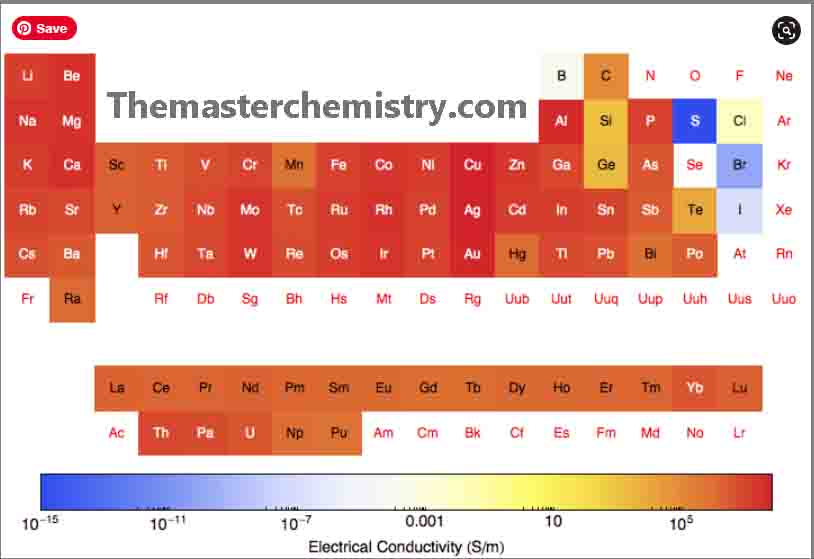
Electrical conductivity of transition elements
The elements of the transition metal series show abrupt changes in the electrical conductance.
However, when we go from left to the right in the periodic table, it indicates an interesting correlation. This is between electrical conductance of the transition elements and it is the ability of the valance electron to form covalent bonds within the elements.
Reasons for high conductivity of group I-A, II-A and III-A
The atoms of these elements contains number of free valence electrons. Therefore, these possess the ability to move around in the crystal structure. These cannot achieve a closed shell electronic configuration even by mutual sharing. For this reason, these show electrical conductivities.
Reasons for low conductance of group V-A, VI-A, and VII-A elements
In these elements, the movement of valence electrons is generally restricted, as they pair up to achieve a close shell configuration. They form the covalent molecules. The value of electrical conductance of these elements are very low.
Electrical conductance of IV-A group elements
The elements of group IV-A i.e., C, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb have intermediate character regarding electrical conductivity.
- Carbon in the form of diamond is a non-conductor, because all of its valence electrons are tetrahedrally bonded, and these cannot move freely.
- Carbon in the form of graphite is shown the property of electrical conductance. Anyhow it shows anisotropic behavior. Electrical current can pass parallel to the sheets. Actually loosely held electrons are available parallel to the sheets for electrical conductivity.
- The lowe elements of the group IV-A such as Sn and Pb are also failry good conductors of electricity. Their electrical conductivities are very close to the elements of group I-A.
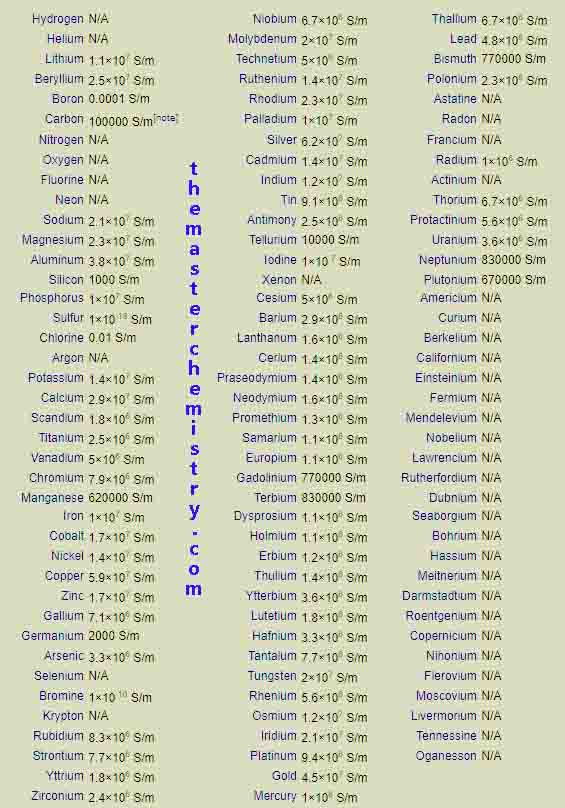
Values of electrical conductivities of elements in periodic table
FAQS
What elements are conductive?
The elements that are conductive are the elements that have the ability to transmit the electric current. These elements will transfer the electric charge from one place to another place. So, these are the elements that are conductive.
Why does electrical conductivity increase down a group?
Electrical conductivity increases down a group because of the increasing size number of electrons of atoms. Further with the increase in atomic size electrons feels less nuclear attraction and tend to become loosely attached. Therefore, electrical conductivity increase down a group.
Why are metals conductive?
Metal atoms have a larger atomic size. Metals have loosely attached electrons in outermost shells. Therefore these electrons transfer electric current and hence metals are conductive.
What makes a metal conductive?
Metals are good conductors of electricity because they have a high concentration of free electrons, which are able to move freely through the metal’s lattice structure. In a metal, the valence electrons, which are the outermost electrons in the atoms, are not tightly bound to a particular atom, but are able to move throughout the metal. This allows them to easily flow through the metal when an electric field is applied, resulting in the metal’s ability to conduct electricity.
What determines conductivity of an element?
The conductivity of an element is determined by the ability of its electrons to move freely through the element. The ease with which the electrons can move is influenced by the element’s crystal structure and the strength of the forces holding the atoms together.
Let other know about this