LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Table of Contents
In this article, the author has explained about Photochemistry, its scope and applications in everyday life.
What is photochemistry?
Photochemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies chemical reactions that are initiated by the presence of light. It primarily examines the effect of light on chemical substances.
Photochemistry involves the study of chemical reactions induced by specific wavelength ranges of electromagnetic radiation, such as the absorption of ultraviolet light (100-400 nm), visible light (400-750 nm), or infrared radiation (750-2500 nm).
This introduction will provide an overview of this topic and show how it relates to other branches of science like physics and biology.
Photochemistry is the chemical study of light and its interactions with matter. Specifically, it entails “the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with any living system that can give rise to electronic excitation followed by molecular fragmentation.
The effect of photochemistry depends on the wavelength of the light used; using short-wavelength UV produces more radical reactions because of the high energy.
History of photochemistry
The word photochemistry is a combination of the words “photo” and “chemistry.” The history of photochemistry begins with the discovery that certain substances are altered by exposure to light.
This theory was first proposed in 1803 when Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel’s experiments proved silver salts are darkened by sunlight. It would be another 50 years before this effect was applied to photographic film, however.
In 1862, Joseph Norman Lockyer observed that when sunlight shone through a prism, it created an image on the screen with seven dark lines across its spectrum. He concluded that these “Fraunhofer Lines” were caused by some element in the sun not present in other stars. Later research determined this unknown substance was hydrogen.
Principle of photochemistry
One of the fundamental principles of photochemistry is that the energy of light is absorbed by matter, and this energy can be used to drive chemical reactions.
When light is absorbed by a molecule, it can excite an electron from its ground state to a higher energy level. This excited state is unstable and the molecule will eventually return to its ground state, releasing the absorbed energy in the form of heat or light.
However, if the molecule is able to transfer this energy to another molecule before returning to its ground state, a chemical reaction can occur.
According to the Woodward-Hoffmann process theory, the absorption of light by a molecule can not only provide the required activation energy but also change the molecule’s electronic configuration symmetry, enabling otherwise inaccessible reaction paths. One example is the 2+2 cycloaddition reaction, which can be studied using these principles or the associated frontier molecular orbital theory.
Photochemical reactions can occur much faster than thermal reactions, with reported reaction times as fast as 109 seconds and associated processes as fast as 1015 seconds.
What is photochemical reaction?
A photochemical reaction is a chemical reaction that is initiated or facilitated by the absorption of light. When light is absorbed by a molecule, it can excite an electron from its ground state to a higher energy level.
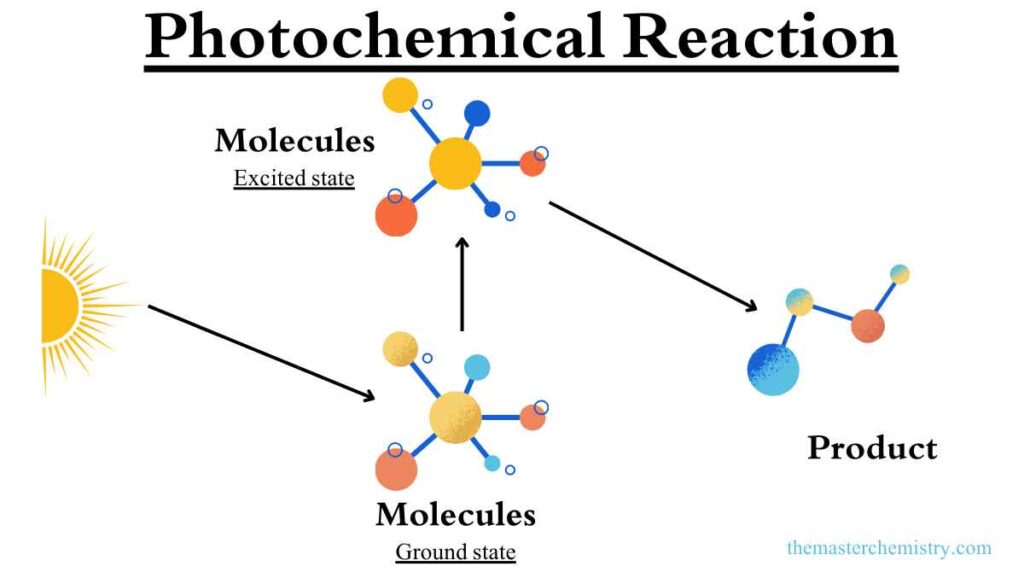
This excited state is unstable, and the molecule will eventually return to its ground state, releasing the absorbed energy in the form of heat or light.
Examples of Photochemical reaction
Here are some examples of photochemical reactions:
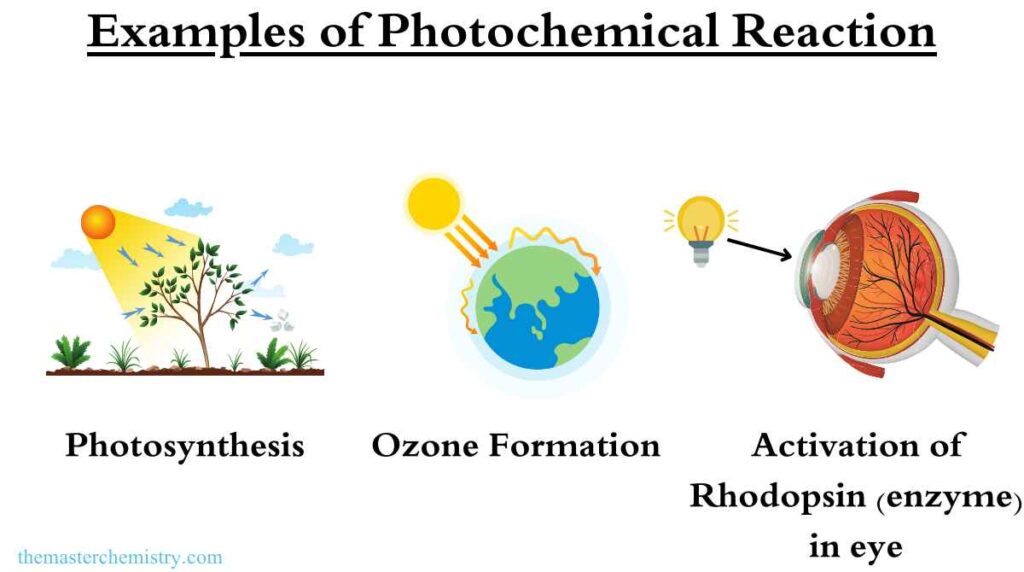
Synthesis of Vitamin D in skin
When UV light is absorbed by the skin, it can initiate the synthesis of vitamin D from cholesterol. This process is important for maintaining healthy bones and teeth.
Bleaching of textiles
Photochemistry is often used in the bleaching of textiles, such as cotton and wool. When these materials are exposed to UV light, the light energy can break the bonds of certain pigments, causing them to fade or disappear.
Formation of ozone in atmosphere
Ozone is formed in the Earth’s atmosphere when UV light is absorbed by oxygen molecules, causing them to split into individual atoms. These atoms can then react with other oxygen molecules to form ozone.
Action of enzymes
Many enzymes are activated by light, and they can use the energy of light to drive chemical reactions that are important for maintaining the functions of the body. For example, rhodopsin, a protein found in the retina of the eye, is activated by light and helps to initiate the process of vision.
Decomposition of food
Photochemistry can also play a role in the decomposition of food. When food is exposed to light, the light energy can break the bonds of certain pigments, causing the food to change color or spoil.
Scope of photochemistry
Photochemistry is a vast and storied field with many practical applications. One of the main branches in photochemistry is concerned with investigating different types of chemical reactions that occur when molecules are exposed to light.
In particular, photochemical studies have been used extensively for research on new drug development as well as solar energy conversion technology. In fact, there are very few areas of chemistry that have not been impacted by the use of photochemistry.
Photochemistry has even been used to study important biological questions like how DNA is repaired. It might seem surprising that the same tool (light) can be utilized for such a wide range of scientific endeavors, but photochemistry continues to provide an exciting research area with many possibilities for future studies in both chemistry and biology.
Applications of photochemistry in everyday life
Applications of photochemistry in everyday life include decontamination of drinking water, production of hydrogen fuel, and food processing.
Photochemical reactions are also used to detect DNA damage or for environmental monitoring.
Also Read: What is the importance of chemistry in everyday life
Another application is the production of light under physiological conditions through photosynthesis with plants or artificial systems based on semiconductor nanomaterials such as quantum dots (QDs) which have unique optical properties compared to organic dyes due to their size-tunable spectrum. These applications will be discussed further below:
Use of photochemistry in decontamination of drinking water
When it comes to the treatment of drinking water, photochemistry is a very important part. It can be used in many different ways including purification and decontamination.

The first example of using the process for decontamination would be UV light being used on bacteria or viruses present in water tanks where no chemicals are able to dissolve properly yet. After this step has been completed, other steps involving filters that remove chemical particles could then take place.
Uses of photochemistry in production of hydrogen fuel
Hydrogen is used in all types of gas turbines. Gas turbine technology is also being developed for vehicles, and these engines are the most efficient type so far available.

The hydrogen fuel cells that power electric cars are another example of photochemistry at work outside a living cell. They use platinum to catalyze energy released by an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen ions (protons) and electrons.
The water molecules needed during this process can be provided by splitting them into their components with additional electricity from solar panels on the vehicle roof or other renewable sources plugged in when parked at home overnight!
Use of photochemistry in food processing
Photochemistry, the use of light for chemical reactions, is common in food processing.

This can be used to either reduce or increase production time or potentially improve quality and it can also be useful when one ingredient cannot easily interact with another without causing a reaction (for example, oil + water). The uses of photochemistry include:
- Draining liquid from brined foods; helps remove any excess salt after curing.
- Sterilization – exposure to ultraviolet radiation kills pathogens present on surfaces such as equipment that comes into contact with ready-to-eat food like salads. It does not interfere with the taste, smell, or texture of the product which makes it an efficient way to keep products safe once they are packed
- Slow down ripening processes by blocking certain wavelengths of light. This is a popular technique for extending the shelf life and improving the quality of foodstuffs such as tomatoes
- Increase shelf life by reducing the amount of oxygen in packaging which prevents oxidative rancidity.
Uses of photochemistry in Medicine
One of the most important uses for photochemistry in medicine is to create a photosensitizer. Photosensitizers are drugs that respond to light by becoming activated and killing cells, sometimes only cancerous cells. This can be used to kill bacteria or viruses, destroy diseased tissues such as tumors, treat skin conditions like psoriasis and eczema, or even combat arthritis.
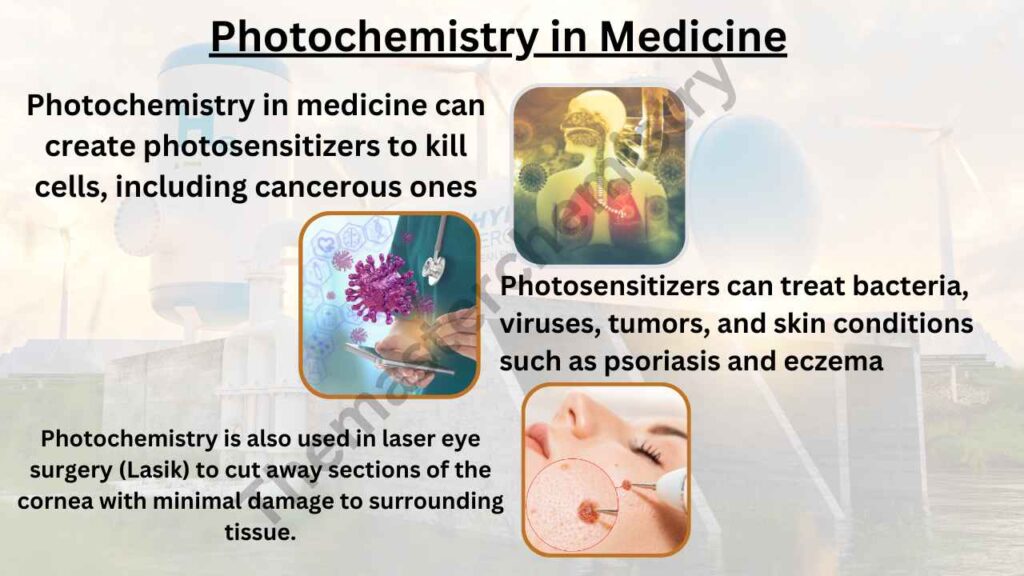
Another medical application where photochemistry plays an important role is laser eye surgery (Lasik). Lasers use light energy at high intensities so that it focuses on very specific parts of your cornea without damaging surrounding tissue. The lasers cut away sections of the cornea using heat generated from photo-acoustic waves caused when photons interact with water molecules.
Uses of photochemistry in Environment protection
There are several ways photochemistry is used to protect the environment.
One way is used to detect and identify pollutants in water. Water molecules that contain impurities absorb ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which results in a change of wavelength for the emitted fluorescent photons.

This can be measured by instruments called fluorometers, which output an electronic signal indicating the presence of certain materials such as sewage or oil spills. The more intense this fluorescence, the higher level of contamination present.
Uses of photochemistry in photograhy
Photochemistry is used in many different applications. For example, silver halide photographic film uses a chemical reaction involving light to create an image on the film.
In modern photography, there are three types of films: black and white negative (neg), color reversal camera negative (reversal) and color print paper positive (print).
Photography is also found in printing processes such as digital photo printers which use lasers to expose photosensitive materials before developing them into prints that can be viewed under visible light or projected onto screens with slide projectors.
Because photochemistry has been around for so long it has become a fundamental process involved in most aspects of everyday life from how we produce food through refrigeration all the way up to advanced scientific research.
Conclusion paragraph
Now that you’re more educated on photochemistry, we hope you’ll be able to better understand how it’s used in your life and the lives of those around you. Want a more detailed explanation? Comment below! We’d love to hear from you about what topics would interest our readers next.
Read More
Forensic Chemistry-Introduction, History, scope and Applications
What is photochemistry, scope and applications
Introduction to Biochemistry-Overview, Scope and Applications
FAQs
Where is photochemistry used?
Photochemistry is used in the decontamination of drinking water, the production of hydrogen fuel, and food processing. Photochemical reactions are also used for detecting DNA damage and environmental monitoring purposes.
what is photochemical phase?
The photochemical phase is the time period during which a photochemical reaction occurs.
What is A photochemical process?
A photochemical process is a chemical reaction initiated or facilitated by the absorption of light. Photochemical processes play a role in a variety of chemical reactions and processes, including the synthesis of vitamin D, the bleaching of textiles, the formation of ozone, and the action of enzymes.
what is photochemical smog?
Photochemical smog is a type of air pollution that is created when sunlight reacts with certain pollutants in the atmosphere. It is typically formed in urban areas with high levels of traffic and industrial activity, where emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are high.
How photochemical reactions have played an important role in photography?
Photochemical reactions have been important in the history of photography, where they were used to create latent images that could be developed into visible ones. These reactions are still used in some forms of photography, such as black and white film photography. However, digital photography, which uses electronic processes, has become more common. Despite this shift, the principles of photochemistry remain important in understanding the interaction of light and matter in photography.