Written by Adeel Abbas
Electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution reactions are two types of substitution reactions that occur in organic chemistry.
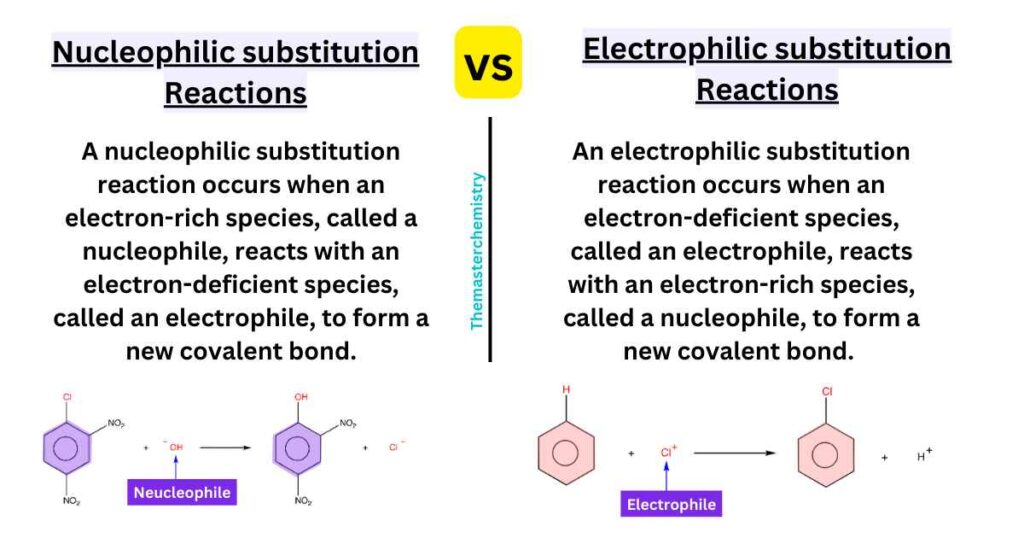
The key difference between electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution reactions is the nature of the reacting species. In electrophilic substitution reactions, an electrophile reacts with a nucleophile, while in nucleophilic substitution reactions, a nucleophile reacts with an electrophile.
Electrophilic vs Nucleophilic substitution Reactions
An electrophilic substitution reaction occurs when an electron-deficient species, called an electrophile, reacts with an electron-rich species, called a nucleophile, to form a new covalent bond. The electrophile is attracted to the electron-rich nucleus of the nucleophile, and the reaction typically occurs at the electrophilic carbon atom. Examples of electrophilic substitution reactions include halogenation of alkanes and alkenes, and the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
A nucleophilic substitution reaction, on the other hand, occurs when an electron-rich species, called a nucleophile, reacts with an electron-deficient species, called an electrophile, to form a new covalent bond. The nucleophile donates a pair of electrons to form a new bond with the electrophile, and the reaction typically occurs at the electrophilic carbon atom. Examples of nucleophilic substitution reactions include the SN1 and SN2 reactions, and the addition of Grignard reagents to aldehydes and ketones.
See the table below to know difference between Electrophilic and Nucleophilic substitution reactions:
| Characteristic | Electrophilic Substitution | Nucleophilic Substitution |
|---|---|---|
| Main Reacting Species | Electrophile (electron-deficient) + Nucleophile (electron-rich) | Nucleophile (electron-rich) + Electrophile (electron-deficient) |
| Bond Formation | Electrophile reacts with nucleophile to form a new covalent bond | Nucleophile donates electrons to form a new covalent bond |
| Reactivity | Electron-deficient species is attracted to the electron-rich nucleus of the nucleophile | Electron-rich species donates electrons to the electron-deficient electrophile |
| Typical Site of Reaction | Occurs at the electrophilic carbon atom | Occurs at the electrophilic carbon atom |
| Examples | Halogenation of alkanes and alkenes, Friedel-Crafts reaction | SN1 and SN2 reactions, addition of Grignard reagents to aldehydes and ketones |