Chapter 3: Gases
In this article, the author has explained the most important chemistry MCQs from the third chapter( Gases) of FSC chemistry. All the correct answers have been highlighted in blue color.
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 1st chapter MCQs
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 2nd chapter MCQs
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 4th chapter MCQs
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 5th chapter MCQs
1: What would be the volume of 10 dm3 of a gas at 0oC temperature and 2.5 atmospheres pressure when it is decomposed to 2 atmospheres pressure, temperature being the same?
A) 1.25 dm3
b) 12.5 dm3
c) 6.3 dm3
d) 18.dm3
2: Which of the following is not true for ideal gases?
a) Pressure of gas is due to collision of molecules with walls of container and with each other
b) Random motion of molecules
c) Follow the general gas equation
d) Molecules show elastic collisions
3: Which of the followings is not true for N2 gas contained in a container at STP?
a) All the molecules have same masses
b) All the molecules possess K.E.
c) All the molecules have same velocities
d) No molecule is stationary
4: Which is not correct for PV/RT ?
a) It is the compressibility factor
b) It is constant for ideal gas at STP for any volume
c) It is a variable for real gases
d) None of these
5: Deviation of gases from the ideal behavior does not depend on
a) Molecular volume
b) Pressure applied
c) Intermolecular
d) None of these
6: Gases cannot be compressed to zero volume because
a) These are incompressible
b) These have repulsive forces
c) Their molecules have non-zero volumes
d) All of these
7: According to the kinetic molecular theory, the gas molecules increase in K.E when they
A) are melted from solid to a liquid state
Are mixed with other molecules at lower temperature
c) Are frozen into solid
d) Are considered into liquid
8: ‘n’ mole of an ideal gas at temperature T (in Kelvin) occupy ‘V’ liters of volume, exerting a pressure of ‘P’ atmospheres. What is its concentration ( in mole/lit)? ( R= gas constant).
a) P/RT
b) PT/R
c) RT/P
d) R/PT
9: All of the following statements are false except
a) Gas molecules do not attract each other at very low temperature
b) Actual volume of a gas is not negligible at very high pressure
c) All of the gas cannot be liquefied
d) Increase in pressure will not decrease the intermolecular distance in a gas
10: At the same temperature and pressure helium is more ideal than hydrogen due to
a) Greater molar mass
b) Greater molecular size
c) Less molar mass
d) Less molecular size
11: A container with a porous wall has mixture of H2, He, N2 and O2. Which of these gases will take maximum time in getting out of the container?
a) H2
b) He
c) N2
d) O2
12: At constant volume for a fixed number of moles of gas, the pressure of the gas increases with the rise in temperature due to;
a) Increase in average molecular speed
b) Increase in molecular attraction
c) Increase in rate of collisions
d) Increase in mean free path
13: An ideal gas expands according to PV= constant. On expansion the temperature of gas
a) will rise
b) will remain constant
c) Will drop
d) Cannot be determined because the external pressure is not known
14: Which curve does not represent Boyle’s law?
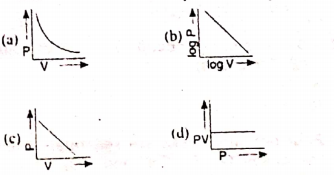
a)
b)
c)
D)
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 6th chapter MCQs
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 7th chapter MCQs
15: At constant temperature and pressure, for equal volumes of O2 and N2
a) No. of moles would be the same
b) No. of atoms would be the same
c) No. of atoms would be the same
d) All of these
16: When 0.5 mole of CO2 and 1 mole of O2, at STP are compressed to two times and three times of their respective original pressure their respective volumes will be
a) 7.5, 6.5
b) 5.6, 7.5
c) 5.6, 5.6
d) None of these
17: In a flask of ‘V’ liters, 0.2 moles of O2, 0.4 moles of N2, 0.1 moles of NH3 and 0.3 moles of He gases are present at 27 0oC. If total pressure exerted by these non-reacting gases is 1 atm, the partial pressure exerted by the gases is in order of;
a) N2>He>O2>NH3
b) He>O2>N2>NH3
c) N2>H2>NH3>O2
d) O2>N2>NH3>He
18: A certain mass of gas occupies a volume of 2 liters at STP. To what temperature the gas must be heated to double its volume keeping the pressure constant?
a) 100K
b) 273K
c) 273 oC
d) 546 oC
19: An unknown gas has a density of 2.45 g/l at 1.5 atmospheric pressure and 25 oC. The gas is
a) Kr
b) Cl2
c) SO2
d) Ar
20: At what centigrade temperature will be the volume of a gas at 0oC doubles of itself, when pressure remains constant?
a) 546 K
b) 273 K
c) 273 oC
d) 0oC
21: A closed container contains equal number of oxygen and hydrogen molecules at a total pressure of 740 mm. If oxygen is removed from the system then pressure will;
a) Become double of 740 nm
b) Become 1/9 of 740 nm
c) Become half of 740 nm
d) Remain unchanged
22: 7.5 grams of gas oCcypy 5.6 liter of volume at STP. The gas is
a) NO
b) N2O
c) CO
d) CO2
23: Four one liter flasks are separately filled with the gases O2, F2, CH4 and CO2 under same conditions. The ratio of the number of molecules in these gases is;
a) 2:2:4:4
b)1:1:1:1
c) 1:2:3:4
d) 2:2:3:4
24: Containers A and B have same gases. Pressure volume and temperature of A are twice that of B, then the ratio of number of molecules of A and B are
a) 1:2
b) 1:4
c) 2:1
d) 4:1
25: If a gas expands at constant temperature
1) the pressure decreases
2) The kinetic energy of the molecules remains the same
3) The kinetic energy of the molecules decreases
4) The number of molecules of the gas increase
a) 1,2
b) 1, 2, 3
c) 1,2, 4
d) 2, 3
26: A bottle of dry ammonia and a bottle of dry hydrogen chloride connected through a long tube are opened simultaneously at both ends, the white ammonium chloride ring first formed will be;
a) At the center of the tube
b) Near the ammonia bottle
c) Near the hydrogen chloride bottle
d) throughout the length of the tube
27: Under which of the following conditions, Van der Waal’s gas approaches ideal behavior?
a) Extremely low pressure
b) High pressure
c) Low product of PV
d) Low temperature
28: Slope of the plot between PV and P at constant temperature is
a) ½
b) 1
c) Zero
d) 1/V2
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 8th chapter MCQs-chemical equilibrium MCQs
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 9th chapter MCQs-Solutions MCQs
Related: FSC 1st year chemistry 10th chapter MCQs-Electrochemistry Mcqs
29: Molar volume of CO2 is maximum at
a) 0oC and 2.0 atm
b) N.T.P
c) 273 oC and 2 atm
d) 127 oC and 1 atm
32: In an open end manometer one end of a U-tube filled with mercury is attached to gas filled container and the other end is open to the atmosphere. If the gas pressure in the container is less than atmospheric pressure
a) the Hg level will be higher in the arm open to the atmosphere
b) Hg will be forced out of the open end of U-tube
c) The difference between the Hg levels in the two arms will be greater than 76 cm
d) The Hg level will be higher in the arm connected to the container
33: Suppose one needs to closely monitor small changes in pressure inside a container using an open end manometer. For the best accuracy, the substance in the manometer should
a) Be mercury
b) Have a low density
c) Have a high density
d) Be a solid
34: If the four tubes of a car are filled to the same pressure with N2, O2 and N2 separately, then which one will be filled first?
a) O2
b) H2
c) Ne
d) N2
35: An ideal gas expands according to PV= constant. On expansion, the temperature of gas
a) will rise
b) Will drop
c) Will remain constant
d) Cannot be determined because the external pressure is not known
36: Some assumptions from the kinetic molecular theory are listed below. Which one is most frequently cited to explain Charles’s law?
a) Collisions of gas particles are elastic and total kinetic energy of the gas is constant
b) A gas consists of tiny particles moving in random straight line motion
c) The volume of the particles is negligible compared to the volume of the gas
d) The average kinetic energy of gas particles is proportional to the Kelvin temperature
37: A closed vessel contains equal number of molecules of O2 and H2. Consider the following statements
1. The average speed of hydrogen molecules will be greater
2. Weight of hydrogen is 1/8th of the weight of oxygen
3. Hydrogen molecule strike the walls more than often
4. The two gases have different average energies
The statements are wrong in
a) 2 and 4
b) 2 and 3
c) 1 and 4
d) 1 and 3
38: At STP which of the following real gases is likely to have smallest molar volume (in m3)?
a) Oxygen
b) Nitrogen
c) Hydrogen
d) Ammonia
39: 6.4g SO2 at 0oC and 0.99 atm pressure occupies a volume of 2.241 L. Predict which of the following is correct?
a) The gas is real with intermolecular attraction
b) The gas is ideal
c) The gas is real without intermolecular attraction
d) The gas is real with intermolecular repulsion greater than intermolecular attraction
41: The total no. of moles of molecules in a mixture formed by intermixing17g of NH3 + 32g of 02 at STP will be
a) 1 mol.
b) 2 moles
c) 6 moles
d) None of these
42: In a mixture containing 44g each of CO2, SO2 and SO3, which of the gases will have largest partial pressure
a) CO2
b) SO2
c) SO3
d) None of these
43: What would be the partial pressure of H2 in a mixture containing 4g H2, 4g He and 28g of N2 contained at 0oC in a container with a volume of 4×22.4 dm3?
a) 1 atm
b) 2 atm
c) 3 atm
d) None of these
44: Which molecules of which of the following gases would move with the slowest speeds in a mixture containing N2, CO, C2H4 and NO?
a) N2
b) CO
c) NO
d) None of these
45: Which of the following does not have the same densities at STP when they have same volumes?
a) N2 and CO
b) O2 and C2H6
c) CO2 and C3H8
d) All of these
46: The relative rates of diffusion of a gas with molecular weight 98 as compared to Hydrogen will be:
a) 1/7
b) 1/5
c) 2/5
d) none
47: Which of the following mixture of gases do not obey Dalton’s law of partial pressure?
a) O2 and CO2
b) Cl2 and SO2
c) N2 and O2
d) NH3 and HCl
48: In which of the following pairs, the critical temperature of latter gaseous species is higher than the first?
a) O2 and CO2
b) Cl2 and SO2
c) N2 and O2
d) NH3 and HCl
49: A and B are ideal gases. The molecular weight of A and B are in ratio1: 4. The pressure of a gas mixture containing equal weights A and B is P atm. What is the partial pressure (in atm) of B in the mixture?
a) P/5
b) P/2
c) P/2.5
d) 3P/4
50: Four rubber tubes are respectively filled with H2, He, N2, and O2. Which tube will be reinflated?
a) H2 filled tube
b) He filled tube
c) N2 filled tube
d) O2 filled tube