Written by Adeel Abbas
Nucleophiles and electrophiles are two important concepts in organic chemistry that describe the reactivity of atoms and molecules in chemical reactions. Nucleophiles are atoms or molecules that have a tendency to donate electrons, while electrophiles are atoms or molecules that have a tendency to accept electrons.
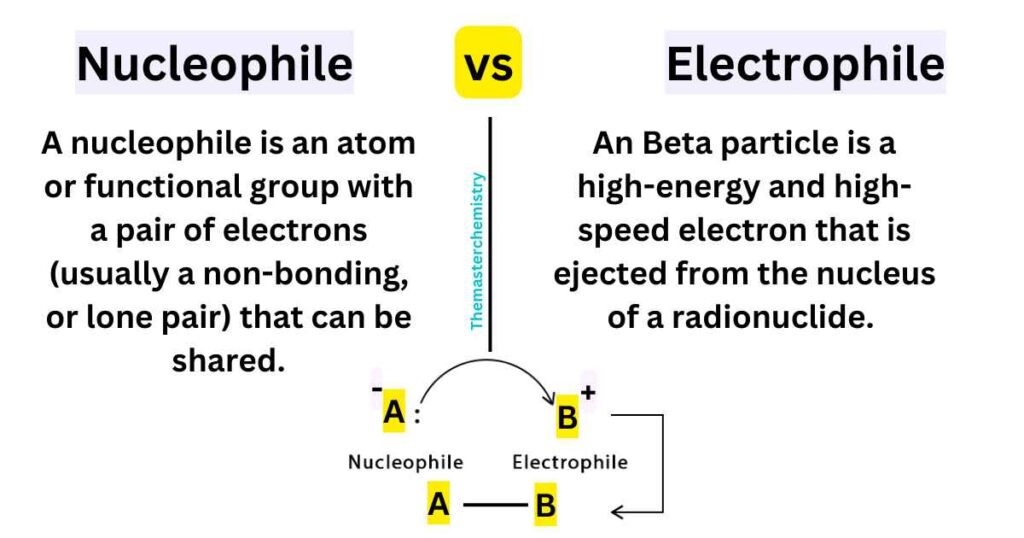
Nucleophile vs Electrophile
The main difference between nucleophiles and electrophiles lies in their electron density. Nucleophiles typically have a high electron density and a negative or partial negative charge, while electrophiles typically have a low electron density and a positive or partial positive charge. This difference in electron density makes nucleophiles and electrophiles react in opposite ways in chemical reactions.
Nucleophiles participate in nucleophilic substitution reactions, which involve the substitution of an atom or group of atoms in a molecule with a nucleophile. For example, in the nucleophilic substitution of halogens (such as Cl or Br) with an amine or alcohol, the nucleophile (amine or alcohol) donates electrons to the electrophile (halogen) and replaces it in the molecule.
On the other hand, Electrophiles participate in electrophilic substitution reactions, which involve the substitution of an atom or group of atoms in a molecule with an electrophile. For example, in the electrophilic addition of H+ to an alkene to form an alkane, the electrophile (H+) accepts electrons from the nucleophile (alkene) and forms a new bond with it.
Another important application of nucleophiles and electrophiles in organic chemistry is in the formation of intermediates species, such as carbocations and carbanions. Carbocations are formed when an electrophile attacks a carbon atom, creating a positive charge on the carbon atom. Carbanions, on the other hand, are formed when a nucleophile attacks a carbon atom, creating a negative charge on the carbon atom.
In summary, nucleophiles and electrophiles play a crucial role in many organic chemical reactions and are widely used in the synthesis of organic compounds. They are characterized by their electron density and their tendency to either accept or donate electrons. Understanding the difference between nucleophiles and electrophiles is essential for understanding the mechanisms of many organic reactions.
See the table below to know difference between electrophile and nucleophile
| Characteristics | Nucleophile | Electrophile |
| Electron density | High | Low |
| Charge | Negative or partial negative | Positive or partial positive |
| Reactivity | Donates electrons in chemical reactions | Accepts electrons in chemical reactions |
| Common reactions | Nucleophilic substitution reactions | Electrophilic substitution reactions |
| Intermediates formed | Carbanions | Carbocations |