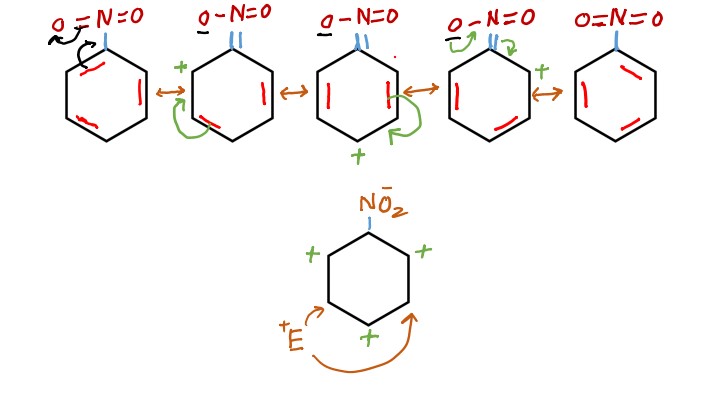
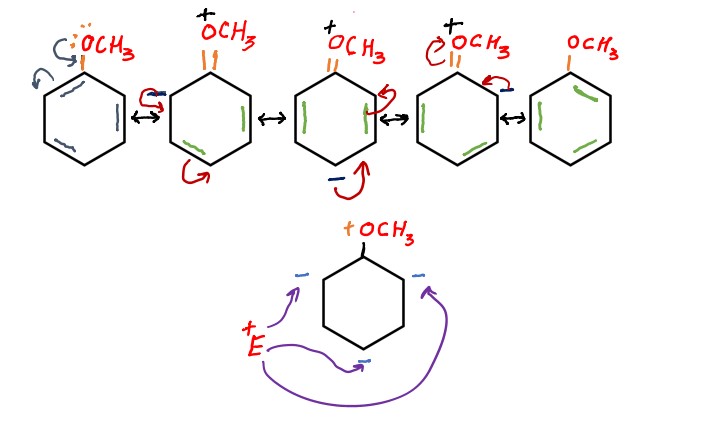
Fundamental principles of organic chemistry You need to know
Written by Adeel Abbas Introduction to organic chemistry Knowing about fundamental principles of organic chemistry is much worthy. Because it is better to know about the priniciples of organic chemistry before diving in organic chemistry books. Historical approach towards organic chemistry In early days of chemistry the scientists were not able to distinguish between organic … Read more